NCERT SCIENCE
CONTROL AND COPORDINATION
1. Which part of a nerve cell contains a
nucleus? 1
(a) Axon (b) Dendrite (c) Cyton (d) Nerve endings
(a) Axon (b) Dendrite (c) Cyton (d) Nerve endings
Answer: (c) Cyton.
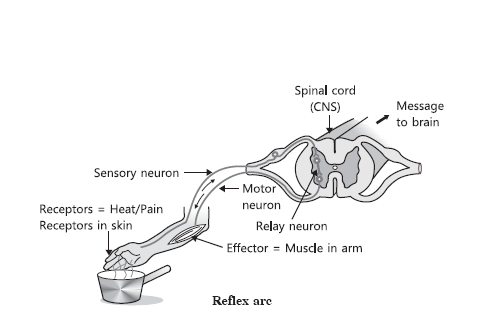
2. The reflex arc is formed by 1
(a) muscle → brain → receptor
(b) muscle → spinal cord → receptor
(c) receptor → brain → muscles
(d) receptor → spinal cord → muscle
(a) muscle → brain → receptor
(b) muscle → spinal cord → receptor
(c) receptor → brain → muscles
(d) receptor → spinal cord → muscle
Answer: (d) receptor → spinal cord → muscle.
3. Which of the following tissues provide
control and coordination in animals? 1
(a) Nervous and Skeletal
(b) Muscular and Skeletal
(c) Muscular and Transport
(d) Nervous and Muscular
(a) Nervous and Skeletal
(b) Muscular and Skeletal
(c) Muscular and Transport
(d) Nervous and Muscular
Answer: (d) Nervous and Muscular
4. A student accidentally places her hand on a
flame of the candle and quickly pulls her hand away. The flame represents 1
(a) a response (b) a stimulus (c) an impulse (d) an effector
(a) a response (b) a stimulus (c) an impulse (d) an effector
Answer: (b) a stimulus.
5. How many pairs of cranial nerves are present
in a man? 1
(a) 12 (b) 21 (c) 31 (d) 41
(a) 12 (b) 21 (c) 31 (d) 41
Answer: (a) 12
6. Reflex actions are mediated through 1
(a) brain (b) effectors (c) spinal cord (d) receptors
(a) brain (b) effectors (c) spinal cord (d) receptors
Answer: (c) spinal cord.
7. The leaves of Mimosa are sensitive to 1
(a) light (b) smell (c) touch (d) heat
(a) light (b) smell (c) touch (d) heat
Answer: (c) touch.
8. Which statement is incorrect about auxins? 1
(a) They promote the growth of root
(b) They promote the growth of shoot
(c) They influence the formation of flower and ripening of fruit
(d) They inhibit the growth of root
(a) They promote the growth of root
(b) They promote the growth of shoot
(c) They influence the formation of flower and ripening of fruit
(d) They inhibit the growth of root
Answer: (a) They promote the growth of the root.
9. The hormone that is used to keep flowers
fresh is 1
(a) cytokinin (b) gibberellins (c) auxin (d) abscisic acid
(a) cytokinin (b) gibberellins (c) auxin (d) abscisic acid
Answer: (a) cytokinin.
10. The main effect of cytokinin in plants is to 1
(a) improve the quality of fruits
(b) prevent the growth of lateral buds
(c) regulate the opening and closing of stomata
(d) stimulate cell division
(e) increase the length of internodes on flowering stems
(a) improve the quality of fruits
(b) prevent the growth of lateral buds
(c) regulate the opening and closing of stomata
(d) stimulate cell division
(e) increase the length of internodes on flowering stems
Answer: (d) increase the length of internodes on
flowering stems.
11. Abscisic acid controls 1
(a) cell elongation and cell wall formation
(b) shoot elongation
(c) cell division
(d) leaf fall and dormancy
(a) cell elongation and cell wall formation
(b) shoot elongation
(c) cell division
(d) leaf fall and dormancy
Answer: (d) leaf fall and dormancy.
12. Which endocrine gland is also known as
‘master gland’? 1
(a) Pancreas (b) Adrenal (c) Pituitary (d) Hypothalamus
(a) Pancreas (b) Adrenal (c) Pituitary (d) Hypothalamus
Answer: (c) Pituitary.
13. Which of the following acts as both
endocrine and exocrine glands? 1
(a) Adrenal (b) Pituitary (c) Ovaries (d) Pancreas
(a) Adrenal (b) Pituitary (c) Ovaries (d) Pancreas
Answer: (d) Pancreas.
14. Which hormone regulates the ionic balance in
the body? 1
(a) Glucagon (b) Thyroxine (c) Testosterone (d) Vasopressin
(a) Glucagon (b) Thyroxine (c) Testosterone (d) Vasopressin
Answer: (d) Vasopressin.
15. Which of the following is not a ductless
gland? 1
(a) Adrenal (b) Liver (c) Thyroid (d) Pituitary
(a) Adrenal (b) Liver (c) Thyroid (d) Pituitary
Answer: (b) Liver.
16. Ageing in human beings is caused by the disappearance of which of the following glands?
1
(a) Adrenal (b) Pituitary (c) Thyroid (d) Thymus
(a) Adrenal (b) Pituitary (c) Thyroid (d) Thymus
Answer: (d) Thymus.
17. Which of the following statements is correct
about receptors? 1
(a) Gustatory receptors detect taste while olfactory receptors detect the smell
(b) Both gustatory and olfactory receptors detect the smell
(c) Auditory receptors detect smell and olfactory receptors detect the taste
(d) Olfactory receptors detect taste and gustatory receptors smell
(a) Gustatory receptors detect taste while olfactory receptors detect the smell
(b) Both gustatory and olfactory receptors detect the smell
(c) Auditory receptors detect smell and olfactory receptors detect the taste
(d) Olfactory receptors detect taste and gustatory receptors smell
Answer: (a) Gustatory receptors detect the taste
while olfactory receptors detect the smell.
18. Which of the following is not associated
with the growth of a plant? 1
(a) Auxin (b) Gibberellins (c) Cytokinins (d) Abscisic acid
(a) Auxin (b) Gibberellins (c) Cytokinins (d) Abscisic acid
Answer: (d) Abscisic acid.
19. Involuntary actions in the body are
controlled by 1
(a) medulla in forebrain
(b) medulla in midbrain
(c) medulla in hindbrain
(d) medulla in the spinal cord
(a) medulla in forebrain
(b) medulla in midbrain
(c) medulla in hindbrain
(d) medulla in the spinal cord
Answer: (c) medulla in the hindbrain.
20. In the following questions, the Assertion
(A) and Reason (R) have been put forward. Read both the statements carefully
and choose the correct alternative from the following: 1
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: Reflex Arc works faster than thinking
process of the brain.
Reason: Reflex Arc works in case of those animals who do not have thinking process.
Reason: Reflex Arc works in case of those animals who do not have thinking process.
Answer: (c) Assertion is true but the Reason is
false.
21. In
the following questions, the Assertion (A) and Reason (R) have been put
forward. Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative
from the following: 1
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: Impulse
travels from dendrite to cell body and then along the axon to its end.
Reason: Information acquired at the end of the dendrite tip of a nerve cell sets of an electric impulse.
Reason: Information acquired at the end of the dendrite tip of a nerve cell sets of an electric impulse.
Answer: (a) Both the
Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation
of the Assertion.
22. In
the following questions, the Assertion (A) and Reason (R) have been put
forward. Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative
from the following: 1
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: Brain is a delicate organ which is protected from injury.
Reason: The bony box protects the brain from any shock.
Reason: The bony box protects the brain from any shock.
Answer: (c) Assertion
is true but the Reason is false.
23. In
the following questions, the Assertion (A) and Reason (R) have been put
forward. Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative
from the following: 1
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: Plants do
have a nervous system for control and coordination.
Reason: Plants use electrochemical means to convey information from cell to cell.
Reason: Plants use electrochemical means to convey information from cell to cell.
Answer: (d) The statement
of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
24. In
the following questions, the Assertion (A) and Reason (R) have been put
forward. Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative
from the following: 1
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: On
attaining puberty, breast size increases and reproductive organs develop in
females.
Reason: Ovaries release hormone progesterone in the female.
Reason: Ovaries release hormone progesterone in the female.
Answer: (b) The
Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct
explanation of the Assertion.
25. The cells in our body that can be over a foot
long are ___________. 1
Answer: nerve cells
26. The box enclosing the brain is called the
_______. 1
Answer: cranium
27. The lobes — parietal, temporal, frontal and
occipital belong to __________. 1
Answer: cerebrum
28. In a neuron, conversion of the electrical signal
to a chemical signal occurs at/in ________.
1
Answer: axonal end
29. Posture and balance of the body is controlled
by __________.
Answer: cerebellum
30. The movement of a shoot towards light is ______. 1
Answer: phototropism
31. The movement of sunflower in accordance with
the path of the sun is due to ________. 1
Answer: phototropism
32. Reflex action is an autonomic motor response
without the involvement of the brain. [True/False]
1
Answer: True.
33. Insulin is given to the person suffering from
goitre. [True/False] 1
Answer: False.
34. Iodine is essential for the synthesis of
thyroxine. [True/False] 1
Answer: True.
35. Plants coordinate their behaviour against
environmental changes by using plant hormones. [True/False] 1
Answer: True.
36. The reaction to stimuli is a characteristic
property of animals only. [True/False] 1
Answer: False.
37. The shoots of a potted plant kept near the
window bend towards sunlight because of negative phototropism. [True/False] 1
Answer: False.
38. A cell or group of cells in a sense organ
which is sensitive to a particular type of stimulus is called a receptor.
[True/False] 1
Answer: True.
39. The hormone which is associated with female
puberty is called testosterone. [True/False] 1
Answer: False.
40. The job of the central nervous system is to
collect all the information from all the receptors in our body. [True/False] 1
Answer: True.
41. Match Column I with Column
II. 1
Column I
|
Column II
|
(i) Neuron
(ii) Cyton (iii) Dendrite (iv) Axon |
(A) Short and branched
(B) Elongated fibre (C) The functional unit of the nervous system. (D) Contains nucleus and cytoplasm |
Answer: (i) (C), (ii) (D), (iii) (A), (iv) (B)
42. Match Column I with Column
II. 1
Column I
|
Column II
|
(i) Photoreceptor
(ii) Gustatoreceptor (iii) Olfactoreceptor (iv) Phonoreceptor |
(A) Smell
(B) Sound (C) Taste (D) Light |
Answer: (i) (D), (ii) (C), (iii) (A), (iv) (B)
43. Name the two components of
central nervous systems in humans. 1
Answer: The two components of the Central Nervous
System in human are the brain and spinal cord.
44. How is the spinal cord
protected in the human body? 1
Answer: Spinal cord is enclosed in a bony cage
called vertebral column.
45. Name two tissues that
provide control and coordination in multicellular animals. 1
Answer: The two tissues that provide control
and coordination in multicellular animals are nervous and muscular tissues.
46. What is the significance of
reflex action? 1
Answer: Reflex action enables the animal to
respond quickly and relieves the brain from excess work.
47. Give one example of
chemotropism. 1
Answer: The growth of pollen tube towards a chemical produced by ovule during fertilisation of flower is an example of
chemotropism.
48. Where are Nissl’s granules
found and what is their nature? 1
Answer: Nissl’s granules are found in cyton
and dendrites. These are formed of ribonucleic acid (RNA).
49. A potted plant is made to
lie horizontally on the ground. Which part of the plant will show 1
(a) positive geotropism?
(b) negative geotropism?
(a) positive geotropism?
(b) negative geotropism?
Answer:
(a) Root
(b) Shoot
(b) Shoot
50. Name any two types of
tropism. 1
Answer: Phototropism and geotropism.
51. Name one plant growth
hormone which retards growth during the extremely dry season. 1
Answer: Abscisic acid
52. A young green plant receives
sunlight from one direction only. What will happen to its shoots and roots? 1
Answer: Shoots will bend towards the light and
roots away from the light.
53. Name the plant hormones
which help/promote (a) cell division (b) growth of the stem. 1
Answer: The plant hormones which help or
promote:
(a) Cell division — Cytokinins
(b) Growth of the stem — Gibberellins
(a) Cell division — Cytokinins
(b) Growth of the stem — Gibberellins
54. Give technical terms for
following events: 1
(a) The movement of the plant in the direction of light.
(b) The movement of plant parts in response to water.
(c) The movement of plant parts towards chemical substance.
(d) The downward movement of roots in response to gravitational force.
(a) The movement of the plant in the direction of light.
(b) The movement of plant parts in response to water.
(c) The movement of plant parts towards chemical substance.
(d) The downward movement of roots in response to gravitational force.
Answer:
(a) Phototropism
(b) Hydrotropism
(c) Chemotropism
(d) Geotropism.
(b) Hydrotropism
(c) Chemotropism
(d) Geotropism.
55. What is the stimulus in 1
(a) Phototropism
(b) Geotropism and
(c) Chemotropism?
(a) Phototropism
(b) Geotropism and
(c) Chemotropism?
Answer:
(a) Light
(b) Gravity
(c) Chemicals.
(b) Gravity
(c) Chemicals.
56. Give an example of a plant
hormone that promotes its growth. Where it is synthesized? 1
Answer: Auxin promotes growth. It is
synthesised at the shoot tip of the plant body.
57. State the function of 1
(a) gustatory receptors, and
(b) olfactory receptors
(a) gustatory receptors, and
(b) olfactory receptors
Answer:
(a) Gustatory receptors receive a taste.
(b) Olfactory receptors receive smell.
(b) Olfactory receptors receive smell.
58. Mention the part of the body
where gustatory and olfactory receptors are located. 1
Answer: Gustatory receptors are located in the cerebrum of fore-brain. Olfactory receptors are located in Olfactory lobe of
fore-brain.
59. Mention the function of the
hind-brain in humans. 1
Answer: Hind-brain
coordinates the body movements and posture. It also controls respiration.
60. Name the fluid that is found
between the meninges.
Answer: Cerebrospinal fluid.
61.
Which part of the brain is concerned
with memory, will and power? 1
Answer: Cerebral hemisphere.
62.
Name the place of the human body where the largest number of neurons are found. 1
Answer: Human brain.
63.
Name the part of the brain which is
concerned with muscular coordination in the body. 1
Answer: Cerebellum.
64.
Name the hormone that helps in
regulating the level of sugar in our blood. Name the gland that secretes it. 1
Answer: Insulin helps in regulating blood
sugar level. This hormone is secreted by the pancreas gland.
65.
Mention the function of adrenaline
hormone. 1
Answer: The function of adrenaline hormone is
to regulate blood pressure, heartbeat, breathing rate, carbohydrate metabolism
and mineral balance in the body.
66.
Name one organ where growth hormone is
synthesized in the case of plants and man. 1
Answer: Shoot tip in plants and pituitary
gland (anterior) in man.
67.
Name the main hormone secreted by
thyroid gland and state its one function.
1
Answer: The main hormone secreted by the thyroid
gland is thyroxine. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and
proteins in the body so as to provide the best growth balance.
68.
Name one gland in the human body which
secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones.1
Answer: Pancreas.
69.
Name the hormone secreted by the alpha
cells of Islets of Langerhans in Pancreas.1
Answer: Glucagon.
70.
Name the hormones that control the
metabolism of calcium and phosphorus. 1
Answer: Calcitonin and Parathormone.
71. Where is glucagon secreted?
What is its function? 1
Answer: Glucagon is secreted in the a-cells of
Islets of Langerhans.
The function of glucagon is to increase the blood glucose level.
The function of glucagon is to increase the blood glucose level.
72. Name the glands which
secrete estrogen and progesterone. 1
Answer: Ovaries.
73. Name the hormone which is
associated with the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, calcium and
phosphorus. 1
Answer: Thyroxine.
74. Name the hormone secreted by the pancreas. State one function. 1
Answer: Insulin and Glucagon.
Its function is to balance the blood glucose level in the body.
Its function is to balance the blood glucose level in the body.
75. Why is pituitary called the
master gland? 1
Answer: The pituitary gland controls the activity of other endocrine glands; so, it is called the master gland.
76. Why hormones are called as
‘chemical messengers’? 1
Answer: Hormones are carried in the blood
streams to all parts of the body, so they are called ‘chemical messengers’.
77. Name the part of the human body
in which the adrenal and pituitary glands are located. 1
Answer:
Adrenal – Above kidney and
Pituitary – Brain.
Pituitary – Brain.
78. Why are endocrine glands
called ductless glands? 1
Answer: Endocrine glands are called ductless
glands because they do not have any external duct to discharge their secretions
into the bloodstream.
79. What are the functions of
the Hypothalamus? 1
Answer: Hypothalamus regulates the secretion
of hormones from the pituitary gland.
80. Why is it advised to use
iodised salt in our diet? 1
Answer: Iodised salt contains iodine which is
necessary for the thyroid gland to synthesise thyroxine hormone. Thyroxine
regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body to provide
growth balance. Its deficiency causes goitre.
81. Name the hormone which regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism
in our body. Which gland secretes this hormone? Why is it important for us to
have iodised salt in our diet? 3
Answer: Thyronine regulates carbohydrates,
protein and fat metabolism in our body.
Thyroxine is secreted from the thyroid gland. Deficiency of iodine in our food causes (goitre) where the thyroid gland to enlarges as it needs to absorbs more amount of iodine. Iodine is required to make thyroxine. Therefore, iodine is added to salt to supplement iodine requirement.
Thyroxine is secreted from the thyroid gland. Deficiency of iodine in our food causes (goitre) where the thyroid gland to enlarges as it needs to absorbs more amount of iodine. Iodine is required to make thyroxine. Therefore, iodine is added to salt to supplement iodine requirement.
82.
(a) Draw the structure of neuron and
label cell body and axon. 3
(b) Name the part of the neuron:
(i) where information is acquired
(ii) through which information travels as an electrical impulse.
(b) Name the part of the neuron:
(i) where information is acquired
(ii) through which information travels as an electrical impulse.
Answer:
(b) (i) Dendrite (ii) Axon
83.
(a) How is the brain protected from injury
and shock? 3
(b) Name two main parts of the hindbrain and state the functions of each.
(b) Name two main parts of the hindbrain and state the functions of each.
Answer:
(a) The brain sits inside a bony box. Inside
the box, the brain is contained in a fluid-filled balloon which provides
further shock absorption.
(b) Two main parts of hindbrain are–Medulla and Cerebellum. Their functions are:
Medulla: Involuntary actions such as blood pressure, salivation and vomiting are controlled by the medulla.
Cerebellum: It is responsible for the precision of voluntary actions and maintaining the posture and balance of the body.
(b) Two main parts of hindbrain are–Medulla and Cerebellum. Their functions are:
Medulla: Involuntary actions such as blood pressure, salivation and vomiting are controlled by the medulla.
Cerebellum: It is responsible for the precision of voluntary actions and maintaining the posture and balance of the body.
84.
State the functions of any three of the
structural and functional unit of the nervous system. 3
Answer: The structural and functional unit of
nervous system i.e. neuron with their functions are as follows:
(i) Cell body: Stimulus received from dendrite is changed into an impulse in the cyton.
(ii) Dendrites: They receive sensation or stimulus, which may be physical, chemical, mechanical or electrical. They pass the stimulus to cyton.
(iii) Axon: It conducts impulse away from the cell body.
(i) Cell body: Stimulus received from dendrite is changed into an impulse in the cyton.
(ii) Dendrites: They receive sensation or stimulus, which may be physical, chemical, mechanical or electrical. They pass the stimulus to cyton.
(iii) Axon: It conducts impulse away from the cell body.
85.
What is a reflex action? Describe the
steps involved in a reflex action. 3
Answer: Reflex Action. It is defined as an unconscious, automatic and involuntary response of effectors, i.e. muscles and
glands, to a stimulus, which is monitored through the spinal cord.
Mechanism of Reflex Action. It involves the following steps :
(i) Receptor organ like skin perceives the stimulus and activates a sensory nerve impulse.
(ii) Sensory organ carries a message in the form of the sensory impulse to the spinal cord.
(iii) The spinal cord acts as a modulator. The neurons of the spinal cord transmit the sensory nerve impulse to the motor neuron.
(iv) Motor nerve conducts these impulses to the effectors like leg muscles which respond by pulling back the organ away from the harmful stimulus.
Mechanism of Reflex Action. It involves the following steps :
(i) Receptor organ like skin perceives the stimulus and activates a sensory nerve impulse.
(ii) Sensory organ carries a message in the form of the sensory impulse to the spinal cord.
(iii) The spinal cord acts as a modulator. The neurons of the spinal cord transmit the sensory nerve impulse to the motor neuron.
(iv) Motor nerve conducts these impulses to the effectors like leg muscles which respond by pulling back the organ away from the harmful stimulus.
86.
State the functions of plant hormones.
Name four different types of plant hormones. 3
Answer: Plant hormones help to coordinate
growth, development and responses in the environment. Four different types of plant
hormones are – Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins and Abscisic acid.
(i) Auxins are the group of plant hormones synthesised at the shoot-tip of the plant body. It promotes cell elongation, root formation, cell division, respiration and other physiological processes like protein synthesis, water uptake and protoplasmic permeability. Auxins also play an important role in the development of seedless fruits.
(ii) Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination and flowering. The maximum concentration of gibberellins is found in fruits and seeds.
(iii) Cytokinins are produced in dividing cells throughout the plant. In mature plants, cytokinins are produced in the root tips and are transported to the shoots. Cytokinins promote cell division and also helps in breaking the dormancy of seeds and buds and regulate the phloem transport. Cytokinins delay the ageing in leaves and promote the opening of stomata.
(iv) Abscisic Acid is a growth inhibitor which reverses the growth-promoting effects of auxins and gibberellins. Its effect includes wilting of leaves. It causes dormancy of seeds. It also promotes the closing of stomata.
(i) Auxins are the group of plant hormones synthesised at the shoot-tip of the plant body. It promotes cell elongation, root formation, cell division, respiration and other physiological processes like protein synthesis, water uptake and protoplasmic permeability. Auxins also play an important role in the development of seedless fruits.
(ii) Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination and flowering. The maximum concentration of gibberellins is found in fruits and seeds.
(iii) Cytokinins are produced in dividing cells throughout the plant. In mature plants, cytokinins are produced in the root tips and are transported to the shoots. Cytokinins promote cell division and also helps in breaking the dormancy of seeds and buds and regulate the phloem transport. Cytokinins delay the ageing in leaves and promote the opening of stomata.
(iv) Abscisic Acid is a growth inhibitor which reverses the growth-promoting effects of auxins and gibberellins. Its effect includes wilting of leaves. It causes dormancy of seeds. It also promotes the closing of stomata.
87. What is a synapse? In a neuron cell how is an electrical impulse created
and what is the role of synapse in this context? 3
Answer: Synapse is the junction between two
adjustment neuron or nerve cells, i.e. between axon ending of one and the dendrite of the next.
Transmission of Nerve Impulse. The information acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a neuron sets off a chemical reaction which creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cyton along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals, which cross the synapse and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. In this way, nerve impulses travel in the body.
Synapse helps in transmitting impulses from one neuron to another.
Transmission of Nerve Impulse. The information acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a neuron sets off a chemical reaction which creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cyton along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals, which cross the synapse and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. In this way, nerve impulses travel in the body.
Synapse helps in transmitting impulses from one neuron to another.
88.
Draw a neat diagram of the human brain and
label on it the following parts: 3
(i) Midbrain (ii) Pituitary gland
(i) Midbrain (ii) Pituitary gland
Answer:
89. Suggest a proof that even unicellular organisms like Amoeba respond to
stimuli. Justify giving two examples that even plants respond to stimuli. 3
Answer: Amoeba
moves towards food and tends to aggregate in moderately warm water. Amoeba and
other protozoa avoid mechanical obstacles. Thus, unicellular organisms respond
to stimuli. Roots of plants move downward in response to gravitational force
and shoots of plants move towards the light. This shows that plants respond to
stimuli.
90.
(a) Which plant hormone is present in
greater concentration in the areas of rapid cell division?
(b) Give one example of a plant growth promoter and a plant growth inhibition. 3
(b) Give one example of a plant growth promoter and a plant growth inhibition. 3
Answer:
(a) Cytokinin is present in greater
concentration in the areas of rapid cell division.
(b) An example of a plant growth promoter is gibberellins and example of a plant growth inhibition is abscisic acid.
(b) An example of a plant growth promoter is gibberellins and example of a plant growth inhibition is abscisic acid.
91.
(a) Explain how auxins help in bending of plant stem
towards light.
(b) State the objective of the experiment for which experimental set up is shown in the given diagram. 3
(b) State the objective of the experiment for which experimental set up is shown in the given diagram. 3
Answer:
(a) When a growing plant detects light, auxin
synthesises at the shoot tip to help the cells to grow longer. When the light comes
from one side, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This
concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the
shoot which is away from light and the plant appears to bend towards the light.
(b) The objective of the experiment is to show the phototropic movement of the plant.
(b) The objective of the experiment is to show the phototropic movement of the plant.
92. What is chemotropism ? Give one example. Name any
two plant hormones and mention their functions. 3
Answer: Chemotropism is the movement of a part
of the plant in response to a chemical stimulus. It can be positive chemotropism
or negative chemotropism.
Example: The growth of pollen tube towards a chemical which is produced by on ovule during the process of fertilisation in a flower.
Two plant hormones with their functions are as follows :
Auxins promote cell elongation, root formation, cell division, respiration and other physiological processes like protein synthesis, etc.
Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination and flowering.
Example: The growth of pollen tube towards a chemical which is produced by on ovule during the process of fertilisation in a flower.
Two plant hormones with their functions are as follows :
Auxins promote cell elongation, root formation, cell division, respiration and other physiological processes like protein synthesis, etc.
Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination and flowering.
93. What is ‘phototropism’? How does it occur in
plants? Describe an activity to demonstrate phototropism. 3
Answer: Phototropism is the directional growth
movement of curvature of plant organs in response to unidirectional exposure to
light.
Phototropism in plants:
Plants bend towards the light when they are exposed to it. The aerial shoots usually grow towards the light, while some aerial roots grow away from light. This the response is controlled by the differential distribution of the plant growth substance auxin in the illuminated part which causes differential growth of the shoot or root.
Activity to demonstrate phototropism:
Phototropism in plants:
Plants bend towards the light when they are exposed to it. The aerial shoots usually grow towards the light, while some aerial roots grow away from light. This the response is controlled by the differential distribution of the plant growth substance auxin in the illuminated part which causes differential growth of the shoot or root.
Activity to demonstrate phototropism:
A conical flask with water is taken and the neck of which is covered by a wire
mesh. 2 or 3 freshly germinated bean seeds are kept on the wire mesh. A cardboard box is taken with one side
open, the flask is kept inside the box so that the open side of the box receives
light from a window. After 2-3 days, it will be seen that shoots bend towards
light and roots away from light.
94. Name the
hormone synthesised at the shoot tips. How does it help the plant response
to light? 3
Answer: A hormone called auxin is synthesised at the shoot tip.
When a growing plant detects light, auxin synthesises at the shoot tip to help the cells to grow longer. When the light comes from one side, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light and the plant appears to bend towards the light.
When a growing plant detects light, auxin synthesises at the shoot tip to help the cells to grow longer. When the light comes from one side, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light and the plant appears to bend towards the light.
95. State how the concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the
shoot which is away from the light? 3
Answer: When
a growing plant detects light auxin, synthesises at the shoot tip to help the
cells to grow longer. When the light comes from one side, auxin diffuses towards
the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells
to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light and the plant
appears to bend towards the light.
96. Write one example each of the following tropic
movements: 3
(a) Positive phototropism
(b) Negative phototropism
(c) Positive geotropism
(d) Negative geotropism
(e) Hydrotropism
(f) Chemotropism
(a) Positive phototropism
(b) Negative phototropism
(c) Positive geotropism
(d) Negative geotropism
(e) Hydrotropism
(f) Chemotropism
Answer:
(a) Positive Phototropism: Movement of the stem of
a plant towards light.
(b) Negative phototropism: Movement of roots away from light.
(c) Positive geotropism: Movement of roots towards gravity.
(d) Negative geotropism: Upward movement of shoots.
(e) Hydrotropism: Growth of roots of a plant towards the water in the soil.
(f) Chemotropism: Growth of pollen tubes towards ovule.
(b) Negative phototropism: Movement of roots away from light.
(c) Positive geotropism: Movement of roots towards gravity.
(d) Negative geotropism: Upward movement of shoots.
(e) Hydrotropism: Growth of roots of a plant towards the water in the soil.
(f) Chemotropism: Growth of pollen tubes towards ovule.
97. Smita’s
father has been advised by a doctor to reduce his sugar intake.
(a) Name the disease he is suffering from and name the hormone whose deficiency causes it.
(b) Identify the gland that secretes it and mention the function of this hormone.
(c) Explain how the time and amount of secretion of this hormone is regulated in the human system. 3
(a) Name the disease he is suffering from and name the hormone whose deficiency causes it.
(b) Identify the gland that secretes it and mention the function of this hormone.
(c) Explain how the time and amount of secretion of this hormone is regulated in the human system. 3
Answer:
(a) He is suffering
from diabetes. Deficiency of insulin causes diabetes.
(b) The pancreas secretes insulin. Insulin helps in regulating blood sugar.
(c) When the sugar level in blood increases, it is detected by the cells of the Pancreas which responds by producing more insulin. As the blood sugar level falls, insulin secretion is reduced.
(b) The pancreas secretes insulin. Insulin helps in regulating blood sugar.
(c) When the sugar level in blood increases, it is detected by the cells of the Pancreas which responds by producing more insulin. As the blood sugar level falls, insulin secretion is reduced.
98. Which organ secretes a hormone when blood
sugar rises in our body? Name the hormone and name one enzyme released by this
organ. 3
Answer:
Pancreas secretes a
hormone when blood sugar rises in our body. Insulin is the hormone released by
this organ and the name of the enzyme is pancreatic juice.
99. Name any
three endocrine glands in the human body and briefly write the function of each of
them. 3
Answer:
Three endocrine glands
with their function in the human body are as follows:
(i) Thyroid gland
Functions: It secretes a hormone called thyroxine which regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body and so provide the best balance for growth.
(ii) Adrenal glands
Functions: It secretes two hormones—adrenalin and corticoids hormones which regulate blood pressure, heartbeat, breathing rate, carbohydrate metabolism and mineral balance.
(iii) Pancreas
Function: It secretes two hormones—insulin and glucagon. Insulin hormone lowers blood glucose. Glucagon hormone increases blood glucose.
(i) Thyroid gland
Functions: It secretes a hormone called thyroxine which regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body and so provide the best balance for growth.
(ii) Adrenal glands
Functions: It secretes two hormones—adrenalin and corticoids hormones which regulate blood pressure, heartbeat, breathing rate, carbohydrate metabolism and mineral balance.
(iii) Pancreas
Function: It secretes two hormones—insulin and glucagon. Insulin hormone lowers blood glucose. Glucagon hormone increases blood glucose.
100. Define ‘hormones’.
Name the hormone secreted by the thyroid. Write its function. Why is the use of
iodised salt advised to us? 3
Answer:
Hormones are the
chemical substances which coordinate and control the activities of living
organisms and also their growth.
The hormone secreted by the thyroid is thyroxine. Its function is to regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth.
The use of iodised salt is advised to us because iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine hormone. Thyroxine regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism which is required for growth. Deficiency of iodine in the body causes disorder like swollen neck and disease called a goitre.
The hormone secreted by the thyroid is thyroxine. Its function is to regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth.
The use of iodised salt is advised to us because iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine hormone. Thyroxine regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism which is required for growth. Deficiency of iodine in the body causes disorder like swollen neck and disease called a goitre.
111. Which
part of the brain controls involuntary actions? Write the function of any two
regions of it. 3
Answer:
Hind-brain controls
the involuntary actions.
The cerebellum controls the coordination of body movement and posture.
Medulla oblongata regulates centre for swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting.
The cerebellum controls the coordination of body movement and posture.
Medulla oblongata regulates centre for swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting.
112. Name the
hormone required for the following. Also mention the name of the endocrine gland
from which that hormone is secreted: 3
(i) Lowering of blood glucose.
(ii) Development of moustache and beard in human males.
(iii) Metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
(i) Lowering of blood glucose.
(ii) Development of moustache and beard in human males.
(iii) Metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
Answer:
Hormone
|
Endocrine Glands
|
|
(i) Lowering of blood glucose
|
Insulin
|
Pancreas
|
(ii) Development of moustache and beard in
human males
|
Testosterone
|
Testis
|
(iii) Metabolism of carbohydrate fats and
protein
|
Thyroxine
|
Thyroid
|
113.
(i) Name the parts labelled
A and B in the neuron drawn above.
(ii) Which part acquires the information in the neuron?
(iii) Through which part does the information travel?
(iv) In what form does this information travel?
(v) Where is the impulse converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission?
(b) Name the hormone secreted by the thyroid. What is its function? Why is the use of iodised salt advisable. 5
(ii) Which part acquires the information in the neuron?
(iii) Through which part does the information travel?
(iv) In what form does this information travel?
(v) Where is the impulse converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission?
(b) Name the hormone secreted by the thyroid. What is its function? Why is the use of iodised salt advisable. 5
Answer:
(a) (i) A – Dendrite. B – Axon
(ii) The information in the neuron is acquired at the end of the dendrite tip.
(iii) The information travels from the dendrite to the cell body and then along the axon to its end.
(iv) The information travels in the form of an impulse.
(v) The impulse is converted into a chemical signal at the end of the axon.
(b) Thyroxine hormone is secreted by the thyroid.
(ii) The information in the neuron is acquired at the end of the dendrite tip.
(iii) The information travels from the dendrite to the cell body and then along the axon to its end.
(iv) The information travels in the form of an impulse.
(v) The impulse is converted into a chemical signal at the end of the axon.
(b) Thyroxine hormone is secreted by the thyroid.
Function of Thyroxine
hormone :
It regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth.
The use of iodised salt is advisable because iodine is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin. In the case of iodine deficiency in our diet, there is a possibility one can suffer from goitre, which is a disease of the swollen neck.
It regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth.
The use of iodised salt is advisable because iodine is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin. In the case of iodine deficiency in our diet, there is a possibility one can suffer from goitre, which is a disease of the swollen neck.
114. Suggest
six reflex actions of the body. Explain how the reflex arc is the same in all
of them. 5
Answer: Six reflex
actions of the body are:
(i) When we see a speeding car moving towards us, we move aside.
(ii) We withdraw our hands on being pricked by a pin.
(iii) We withdraw our hands on touching very hot substance.
(iv) We close our eyes on seeing the direct sun or extremely bright source of light.
(v) We close our eyes on hearing a loud noise.
(vi) We shiver on feeling cold.
Reflex arc in all the above cases is the same because in all the cases, the stimulus is received by sense organs. Then this information is carried to the spinal cord through sensory nerves. Thus, information from the spinal cord is sent to the effectors such as muscles via motor neurons.
(i) When we see a speeding car moving towards us, we move aside.
(ii) We withdraw our hands on being pricked by a pin.
(iii) We withdraw our hands on touching very hot substance.
(iv) We close our eyes on seeing the direct sun or extremely bright source of light.
(v) We close our eyes on hearing a loud noise.
(vi) We shiver on feeling cold.
Reflex arc in all the above cases is the same because in all the cases, the stimulus is received by sense organs. Then this information is carried to the spinal cord through sensory nerves. Thus, information from the spinal cord is sent to the effectors such as muscles via motor neurons.
115. What is a
reflex arc? Draw a neat labelled diagram of the components in a reflex arc. Why
do impulses flow only in one direction in a reflex arc? 5
Answer:
The reflex arc is the
pathway taken by the nerve impulses and responses in a reflex action, i.e. from
the receptor organs like skin to the spinal cord and from the spinal cord to
the effector organs like muscles.
Impulses flow only in
one direction in a reflex arc, because each synapse in the reflex arc allows
impulses to cross it in a single direction.
116. What is
meant by reflex-action? With the help of a labelled diagram trace the sequence
of events which occur when we touch a hot object. 5
Answer: Reflex action
is defined as unconscious, the automatic and involuntary response of effector,
i.e. muscle and gland to a stimulus which is monitored through the spinal cord.
The sequence of events
when we touch a hot object is:
(a) Receptor organ skin receives the stimulus and activates a sensory nerve impulse.
(b) Sensory neuron carries the message in the form of a sensory impulse to the spinal cord.
(c) The spinal cord acts as a modulator. The neuron of the spinal cord transmits the sensory nerve impulses to the motor neuron.
(d) Motor nerve conducts these impulses to the effector organ hand which responds by pulling back the hand away from the hot object.
(a) Receptor organ skin receives the stimulus and activates a sensory nerve impulse.
(b) Sensory neuron carries the message in the form of a sensory impulse to the spinal cord.
(c) The spinal cord acts as a modulator. The neuron of the spinal cord transmits the sensory nerve impulses to the motor neuron.
(d) Motor nerve conducts these impulses to the effector organ hand which responds by pulling back the hand away from the hot object.
117. Define
tropism. Explain four kinds of tropisms with one example each. 5
Answer: Tropism is the
mechanism by which plant moves in response to a specific stimulus. If the plant is
moving towards the light it is called positive phototropism. When the plant is
moving away from the light it is called negative phototropism. e.g. stem of the plant moving towards light or sunlight (positive phototropism). Roots of a
plant moving away from light, therefore it shows negative phototropism.
118. With the help of a flow chart, highlight the various types of plant movements with
suitable examples.
Answer:
119. (a) Name
the hormone which is released into the blood when its sugar level rises. Name
the organ which produces this hormone and its effect on blood sugar level. Also
mention the digestive enzymes secreted by this organ with one function of each.
(b) Explain the need of Chemical communication in multicellular organisms. 4
(b) Explain the need of Chemical communication in multicellular organisms. 4
Answer:
(a) When sugar level
rises, the hormone insulin is released into the blood. Insulin is released in our body
by the pancreas. When insulin is secreted in lower quantity by the pancreas, the blood
sugar level of the concerned person increases. On the other hand, if the insulin
is secreted in excess, the person suffers from low sugar in the blood.
(b) Chemical communication is required in multicellular organisms to deal with emergency demand such as infection, traumas, dehydration, starvation, haemorrhage, extreme temperature, etc.
(b) Chemical communication is required in multicellular organisms to deal with emergency demand such as infection, traumas, dehydration, starvation, haemorrhage, extreme temperature, etc.
120. A young boy met an accident while riding a bike. Patrolling police found the boy and
brought him to a hospital for treatment. After the accident, the boy lost his
memory completely. The left side of his body also suffered from paralysis.
(a) What values were shown by police persons?
(b) Which injured body part can cause paralysis?
(c) What precaution should one take while riding a two-wheeler? 4
(a) What values were shown by police persons?
(b) Which injured body part can cause paralysis?
(c) What precaution should one take while riding a two-wheeler? 4
Answer:
(a) The values showed
by the police persons were truthful to duty and humanity.
(b) Injury to the brain or spinal cord can cause paralysis.
(c) Riders must wear helmets while riding a two-wheeler. One must drive in a controlled speed to avoid the accident.
(b) Injury to the brain or spinal cord can cause paralysis.
(c) Riders must wear helmets while riding a two-wheeler. One must drive in a controlled speed to avoid the accident.
121. Mr Bora
has a habit to iron his shirt every morning before going to the office. One morning
he forgot to keep the hot iron in the proper place and left for office. His two years
old daughter touched the iron and her hand got burnt. Mrs Bora immediately put
the hand of her daughter under a running tap as first aid. 4
(a) What value was shown by Mrs Bora?
(b) How do we react when we touch a hot object?
(c) What other materials commonly cause burn injury?
(a) What value was shown by Mrs Bora?
(b) How do we react when we touch a hot object?
(c) What other materials commonly cause burn injury?
Answer:
(a) Mrs Bora showed
the value of adequate knowledge on a subject and capability to use it when
required.
(b) We immediately remove the hand from the hot object due to reflex action.
(c) Hot running water, hot tea/coffee/milk/water, hot cooking ware, hot food items and hot electrical appliances are other common materials which commonly cause burn injury.
(b) We immediately remove the hand from the hot object due to reflex action.
(c) Hot running water, hot tea/coffee/milk/water, hot cooking ware, hot food items and hot electrical appliances are other common materials which commonly cause burn injury.
122. You along
with your parents went to visit the house of your uncle on a weekend. Your aunt
has a very good aesthetic sense and she keeps her house beautifully. She had
kept a few potted plants in the drawing-room. Your aunt, however, complained that
the plants were not keeping straight. All the plants were bending towards one
direction. 4
(a) What can be the reason behind the bending of the plants?
(b) How can your aunt keep the plants straight?
(c) Do animals also show such movements?
(d) What values are possessed by your aunt?
(a) What can be the reason behind the bending of the plants?
(b) How can your aunt keep the plants straight?
(c) Do animals also show such movements?
(d) What values are possessed by your aunt?
Answer:
(a) The plants have
bent due to phototropism. The light might have fallen on the plants from a window
due to which all the plants have bent towards the direction of the light, i.e.
phototropism.
(b) She can keep the plants outdoor for an interval to keep them straight.
(c) No. Animals do not show phototropism.
(d) She is a nature-loving person.
(b) She can keep the plants outdoor for an interval to keep them straight.
(c) No. Animals do not show phototropism.
(d) She is a nature-loving person.
123. The pharmacist from the nearby pharmacy visits your house every morning. He gives
an injection to your grandfather and then proceeds towards his pharmacy. When
asked, he told you that your grandfather was suffering from diabetes. 4
(a) What happens when a person suffers from diabetes?
(b) What complications may diabetes cause to your grandfather?
(c) How can the injection be given by the pharmacist help your grandfather?
(d) What values are shown by a pharmacist?
(a) What happens when a person suffers from diabetes?
(b) What complications may diabetes cause to your grandfather?
(c) How can the injection be given by the pharmacist help your grandfather?
(d) What values are shown by a pharmacist?
Answer:
(a) When a person
suffers from diabetes, his blood sugar level increases.
(b) If blood sugar is consistently high, over time it can affect the heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and other parts of the body. A person suffering from diabetes cannot undergo any operation unless his blood sugar level is brought down with medication before the operation.
(c) The injection given by the pharmacist is insulin injection. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas which helps in regulating blood sugar. In the case of my grandfather, the pancreas is not able to release an adequate quantity of insulin hormone and hence his blood sugar level is high. Insulin provided externally will help in regulating his blood sugar level.
(d) He is a responsible person and who serves people.
(b) If blood sugar is consistently high, over time it can affect the heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and other parts of the body. A person suffering from diabetes cannot undergo any operation unless his blood sugar level is brought down with medication before the operation.
(c) The injection given by the pharmacist is insulin injection. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas which helps in regulating blood sugar. In the case of my grandfather, the pancreas is not able to release an adequate quantity of insulin hormone and hence his blood sugar level is high. Insulin provided externally will help in regulating his blood sugar level.
(d) He is a responsible person and who serves people.

















0 comments:
Post a Comment