Life process
TEST PAPER
CHAPTER: LIFE PROCESS
1.
Autotrophic organisms include 1
(a) bacteria and virus (b) bacteria and fungi
(c) green plants and some bacteria (d) green plants and all bacteria
(a) bacteria and virus (b) bacteria and fungi
(c) green plants and some bacteria (d) green plants and all bacteria
Answer: (c)
2.
A gland not associated with the alimentary canal is 1
(a) liver (b) salivary glands
(c) pancreas (d) adrenal
(a) liver (b) salivary glands
(c) pancreas (d) adrenal
Answer: (d)
3.
Which of the following is chiefly
digested in the stomach? 1
(a) Carbohydrates (b) Proteins
(c) Lipids (d) Fats
(a) Carbohydrates (b) Proteins
(c) Lipids (d) Fats
Answer: (b)
4.
From the given picture of the digestive system, identify the part labelled as a gastric gland. 1
Life process
(a) A (b) B (c) C (d)
D
Answer: (b)
5. The large intestine in man mainly carries
out 1
(a) absorption (b) assimilation
(c) digestion of fats (d ) digestion of carbohydrates
(a) absorption (b) assimilation
(c) digestion of fats (d ) digestion of carbohydrates
Answer: (a)
6.
The part of the digestive system where
no digestion takes place is 1
(a) ileum (b) stomach
(c) mouth (d) oesophagus
(a) ileum (b) stomach
(c) mouth (d) oesophagus
Answer: (d)
7.
The fermentation of glucose by yeast
normally yields 1
(a) alcohol, CO2 and 36 ATP
(b) CO2, H2O and 36 ATP
(c) alcohol, CO2 and 2ATP
(d) lactic acid, CO2 and 2 ATP
(a) alcohol, CO2 and 36 ATP
(b) CO2, H2O and 36 ATP
(c) alcohol, CO2 and 2ATP
(d) lactic acid, CO2 and 2 ATP
Answer: (c)
8.
A large quantity of one of the
following is removed from our body by lungs:
1
(a) CO2 and H2O (b) CO2 only
(c) H2O only (d) ammonia
(a) CO2 and H2O (b) CO2 only
(c) H2O only (d) ammonia
Answer: (a)
9.
In respiration, air passes through 1
(a) Pharynx → nasal cavity → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles
(b) Nasal cavity → pharynx → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles
(c) Larynx → nasal cavity → pharynx → trachea
(d) Larynx → pharynx → trachea → lungs
(a) Pharynx → nasal cavity → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles
(b) Nasal cavity → pharynx → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles
(c) Larynx → nasal cavity → pharynx → trachea
(d) Larynx → pharynx → trachea → lungs
Answer: (b)
10.
A biochemical compound that readily
combines with oxygen and distributes it throughout the human body is 1
(a) water (b) urea
(c) haemoglobin (d) acetylcholine
(a) water (b) urea
(c) haemoglobin (d) acetylcholine
Answer: (c)
11.
The process in which loss of water
takes place in the form of water vapour through stomata is called 1
(a) transportation (b) transpiration
(a) transportation (b) transpiration
(c) guttation (d)
translocation
Answer: (b)
12.
In a closed circulatory system, blood
is completely enclosed within 1
(a) vessels (b) heart
(c) skeleton (d) sinuses
(a) vessels (b) heart
(c) skeleton (d) sinuses
Answer: (b)
13.
Normal blood pressure
(systolic/diastolic) is 1
(a) 120/80 mm of Hg (b) 160/80 mm of Hg
(c) 120/60 mm of Hg (d) 180/80 mm of Hg
(a) 120/80 mm of Hg (b) 160/80 mm of Hg
(c) 120/60 mm of Hg (d) 180/80 mm of Hg
Answer: (a)
14.
Blood pressure is measured by an instrument
called 1
(a) barometer (b) sphygmomanometer
(c) photometer (d) manometer
(a) barometer (b) sphygmomanometer
(c) photometer (d) manometer
Answer: (b)
15.
Which of the following statements is
not correct? 1
(a) Deoxygenated blood is poured into the right atrium of the heart.
(b) The excretory units of flatworms are flame cells.
(c) Human kidney has about 1 million nephridia
(d) Tracheids and vessels are non-living conducting tissues.
(a) Deoxygenated blood is poured into the right atrium of the heart.
(b) The excretory units of flatworms are flame cells.
(c) Human kidney has about 1 million nephridia
(d) Tracheids and vessels are non-living conducting tissues.
Answer: (c)
16.
Which part of alimentary canal receives
bile from the liver? 1
(a) Stomach (b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine (d) Oesophagus
(a) Stomach (b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine (d) Oesophagus
Answer: (b)
17.
When air is blown from the mouth into a
test-tube containing lime water, the lime water turns milky due to the presence
of 1
(a) oxygen (b) carbon dioxide
(c) nitrogen (d) water vapour
(a) oxygen (b) carbon dioxide
(c) nitrogen (d) water vapour
Answer: (b)
18.
The filtration units of kidneys are
called 1
(a) ureter (b) urethra
(c) neurons (d) nephrons
(a) ureter (b) urethra
(c) neurons (d) nephrons
Answer: (d)
19.
Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis
comes from 1
(a) water (b) chlorophyll
(c) carbon dioxide (d) glucose
(a) water (b) chlorophyll
(c) carbon dioxide (d) glucose
Answer: (a)
20.
The opening and closing of the stomatal
pore depends upon 1
(a) oxygen (b) temperature
(c) water in guard cells (d) the concentration of CO2 in stomata
(a) oxygen (b) temperature
(c) water in guard cells (d) the concentration of CO2 in stomata
Answer: (c)
Life process
20.
The opening and closing of the stomatal
pore depends upon 1
(a) oxygen (b) temperature
(c) water in guard cells (d) the concentration of CO2 in stomata
(a) oxygen (b) temperature
(c) water in guard cells (d) the concentration of CO2 in stomata
Answer: (c)
21.
In the following questions, the
Assertion and Reason have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and
choose the correct alternative from the following: 1
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: When air is passed through lime water,
lime water turns milky.
Reason: Air contains 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen.
Reason: Air contains 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen.
Answer: (b) The Assertion and the Reason are
correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
22.
In the following questions, the
Assertion and Reason have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and
choose the correct alternative from the following: 1
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: Veins have thin walls to collect blood
from different organs.
Reason: Blood in veins are not under pressure.
Reason: Blood in veins are not under pressure.
Answer: (a) Both the Assertion and the Reason
are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
23.
In the following questions, the
Assertion and Reason have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and
choose the correct alternative from the following: 1
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: Human being has a complex respiratory
system.
Reason: Human skin is impermeable to gases.
Reason: Human skin is impermeable to gases.
Answer: (b) The Assertion and the Reason are
correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
24.
In the following questions, the
Assertion and Reason have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and
choose the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: All proteins in our food are digested in
small intestine only.
Reason: The protein-digesting enzymes are released onto small intestine.
Reason: The protein-digesting enzymes are released onto small intestine.
Answer: (d) The statement of the Assertion is
false but the Reason is true.
25.
In the following questions, the
Assertion and Reason have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and
choose the correct alternative from the following: 1
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion: Human heart does not allow mixing of
oxygen to reach blood with carbon dioxide reach the blood.
Reason: Human heart has different chambers.
Answer: (a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Reason: Human heart has different chambers.
Answer: (a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Life process
26.
The __________ is where the respiratory
and digestive passage come together. 1
Answer: pharynx.
27.
The conditions necessary for
photosynthesis to take place are________, _______, _______ and _________. 1
Answer: sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide
and water.
28.
The process in which the digested food
passes through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream is called _________. 1
Answer: absorption.
29.
The teeth covered with a sticky,
yellowish layer of food particles and bacteria are called _________.
Answer: plaque.
30.
Iodine turns blue-black on reacting
with _________. 1
Answer: starch.
31.
The energy produced during respiration
is stored in the form of ATP which stands for _________. 1
Answer: Adenosine Tri-phosphate.
32.
Pyruvic acid is a three-carbon compound
which is also known as _________. 1
Answer: pyruvate.
33.
The rate of breathing in _________
animals in much faster than in _________ animals. 1
Answer: aquatic, terriestial
34.
The actual exchange of gases takes
place in the _________ of the lungs. 1
Answer: alveoli.
35.
_________ are long, thin, spindle-shaped cell with pits in their thick cell walls. 1
Answer: Tracheids.
36.
The liquid part of blood is called
_________. 1
Answer: plasma.
37.
The expansion of an artery each time
the blood is forced into it is called _________. 1
Answer: pulse.
Answer: pulse.
38.
Gums and resins are the _________
products of plants. 1
Answer: waste.
39.
Match Column I with Column II. 1
Column I
|
Column II
|
Animal
|
Respiratory Organ
|
(i) Fish
|
(A) Trachea
|
(ii) Birds
|
(B) Gills
|
(iii) Aquatic Arthropoda
|
(C) Lungs
|
(iv) Earthworm
|
(D) Moist cuticle
|
Answer: (i) (B), (ii) (C), (iii) (A), (iv) (D).
40.
Match Column I with Column II. 1
Column I
|
Column II
|
Region of
digestive system |
Digestive juice
|
(A) Mouth
(B) Stomach (C) Duodenum (D) Small intestine |
(i) Pancreatic juice
(ii) Intestinal juice (iii) Gastric juice (iv) Saliva |
Answer: (A) (iv), (B) (iii), (C) (i), (D) (ii).
Life process
41.
Glomerulus acts as a dialysis bag.
[True/False] 1
Answer: True.
42.
Bowman’s capsule is found in the heart.
[True/False] 1
Answer: False.
43. The peristaltic movement of muscles occurs in
the mouth to push food into the alimentary canal. [True/False] 1
Answer: False.
44.
The release of energy in aerobic
process is less than in the anaerobic process. [True/False] 1
Answer: False.
45.
Before testing for starch, chlorophyll
has to be removed from the leaf as it interferes in the test for starch due to
its green colour. [True/False] 1
Answer: True.
46.
The process in which the absorbed food
is taken in by body cells and used for energy, growth and repair is called
egestion. [True/False] 1
Answer: False.
47.
The length of the small intestine in a
human adult is about 3.5 m. [True/False]
1
Answer: False.
48.
Carbohydrates are the components of our
food which is digested by an enzyme which is present in saliva as well as in
pancreatic juice. [True/False] 1
Answer: True.
49. The cytoplasm is the sites of aerobic
respiration in the cells. [True/False]
1
Answer:
False.
50.
The respiration in plants occurs at a
fast rate whereas the respiration in animals occurs at a much slower rate.
[True/False] 1
Answer: False.
51. Mention the raw materials required for photosynthesis. 1
Answer: The
raw materials required for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
52. Mention how organisms like bread moulds and mushrooms obtain their food. 1
Answer: Organisms
like bread moulds and mushrooms break down the food materials outside the body
and then absorb it.
53. Name the green dot-like structures in some cells observed by a student
when a leaf peel was viewed under a microscope. What is this green colour due
to? 1
Answer: The
green dot-like structures in some cells observed by a student when a leaf peel
was viewed under a microscope are chloroplasts. The green colour is due to the
presence of green pigment, chlorophyll.
54. In the experiment “Light is essential for photosynthesis”, why does the
uncovered part of the leaf turn blue-black after putting iodine solution? 1
Answer: Starch
is produced in the uncovered part of the leaf which turns blue-black in
presence of iodine solution.
55.
Name one accessory pigment and one
essential pigment in photosynthetic plants. 1
Answer:
Accessory pigment – Carotene/Xanthophyll
Essential pigment – Chlorophyll
Essential pigment – Chlorophyll
56.
Where does digestion of fat take place
in our body? 1
Answer: Digestion of fat takes place in the small intestine of our body.
57.
Which pancreatic enzyme is effective in
digesting proteins? 1
Answer: Trypsin is the pancreatic enzyme which
is effective in digesting proteins.
58.
Which enzyme present in saliva breaks
down starch? 1
Answer: The saliva contains an enzyme called
salivary amylase that breaks down starch.
59. Mention two structural features of the small intestine which add to the
absorptive capacity. 1
Answer: Two structural features of small
intestine are:
(i) Villi is present to increase the absorptive surface area.
(ii) Lacteals in the villi receive the products of fat digestion.
(i) Villi is present to increase the absorptive surface area.
(ii) Lacteals in the villi receive the products of fat digestion.
60. Give one reason why multicellular organisms require special organs for the exchange of gases between their body and their environment. 1
Answer: Multicellular
organisms need more O2 to perform various body functions. They, therefore, have special organs for exchange of gases.
Life process
61. State the basic difference between the process of respiration and
photosynthesis. 1
Answer: Respiration uses O2 and
releases CO2 but in photosynthesis, CO2 is used
and O2 is released.
62.
Name the intermediate and the end products
of glucose breakdown in aerobic respiration. 1
Answer: Glucose → Pyruvate + Energy CO2 + H2O + Energy
Answer: Glucose → Pyruvate + Energy CO2 + H2O + Energy
63. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for
photosynthesis? 1
Answer: Plants
get carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through stomata and water from the soil through
roots and transport to leaves.
64. What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have
with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration? 1
Answer: The
amount of oxygen dissolved in water is very low, as compared to the amount of
oxygen in the air. Thus, the terrestrial organism has to make fewer efforts to obtain
oxygen than an aquatic organism to obtain oxygen for respiration.
65. Name the two ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in
various organisms. 1
Answer: The two ways in which glucose is
oxidised to provide energy in various organisms are aerobic respiration pathway
which uses oxygen to break-down glucose completely into carbon dioxide and
water and some use other pathways that do not involve oxygen which is called
anaerobic respiration pathway.
66.
Specify two conditions in which
photo-respiration may take place in green plants. 1
Answer: Two conditions in which
photorespiration may take place in green plants are:
(i) The high concentration of oxygen and
(ii) The high temperature
67.
Name the fundamental process in which
living organisms release energy within their cytoplasm. 1
Answer: Respiration.
68.
Give one point which is common for both
aerobic and anaerobic respiration. 1
Answer: In both aerobic and anaerobic
respiration, the chemical used is glucose.
69.
Why is anaerobic respiration less
efficient? 1
Answer: Anaerobic respiration is the
incomplete breakdown of glucose and produces less energy, so it is less
efficient.
70.
Find the odd one out: (a) Trachea,
Bronchus, Alveolus, Diaphragm. (b) Epiglottis, Trachea, Malpighian corpuscles,
Alveoli. 1
Answer: (a) Diaphragm, (b) Malpighian corpuscles.
71.
What is the main function of Adam’s
apple? 1
Answer: To produce voice in the presence of
air.
72. Why are lungs divided into very small sac-like structures called alveoli? 1
Answer: Lungs
are divided into small sacs or alveoli to increase the surface area through
which respiratory exchange takes place.
73. Why do mammals require more extensive respiratory surface? 1
Answer: Mammals
need more oxygen to meet the requirement of their high metabolic rate.
Therefore, they need extensive respiratory surface.
74. What will happen if the diaphragm of a person gets ruptured in an
accident? 1
Answer: Immediate
death due to failure of the respiration.
75. Name the component of blood that helps in the formation of a blood clot in
the event of a cut. 1
Answer: Platelet.
Life process
76. Normally a vein opens into a large vein or into the heart but does not
end in capillaries. Which one or more veins in humans is/are the exception(s) to
this rule? 1
Answer: Hepatic Portal Vein, Hypophyseal Portal Vein.
77. Which pigment is responsible for the transport of nutrients, respiratory
gases, metabolites, hormones and waste products? 1
Answer: Haemoglobin.
78. Write one function of blood platelets in human beings. 1
Answer: They
help in the coagulation of blood and are called thrombocytes.
79. Name the phase of the cardiac cycle in which both auricles and ventricles
are relaxed simultaneously. 1
Answer: Diastole.
80.
Why is the plasma of blood straw-coloured? 1
Answer: Because red blood corpuscle is absent.
Life process
81. What is ‘translocation’ in plants?
1
Answer: Transport
of soluble products of photosynthesis is known as translocation.
82.
Name the tissue which transports
soluble products of photosynthesis in a plant.
1
Answer: Phloem transports soluble products of
photosynthesis in a plant.
83.
Name the tissue which transports water
and mineral in a plant. 1
Answer: Xylem transports water and minerals in
a plant.
84. Why is urine yellow in colour? 1
Answer: Urine
contains urea, uric acid and ammonical salts which imparts yellow colour.
85.
(a) Name the process by which
autotrophs prepare their own food. 3
(b) List the three events which occur during this process.
(c) State two sources from which plants obtain nitrogen for the synthesis of proteins and other compounds.
(b) List the three events which occur during this process.
(c) State two sources from which plants obtain nitrogen for the synthesis of proteins and other compounds.
Answer:
(a) The process by which autotrophs prepare
their own food is called photosynthesis.
(b) The three events which occur during the process of photosynthesis are as follows:
(i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and water.
(iii) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
(c) The two sources from which plants obtain nitrogen for the synthesis of proteins and other compounds are—
(i) Inorganic nitrates or nitrites.
(ii) Organic compounds prepared by bacteria from atmospheric nitrogen.
(b) The three events which occur during the process of photosynthesis are as follows:
(i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and water.
(iii) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
(c) The two sources from which plants obtain nitrogen for the synthesis of proteins and other compounds are—
(i) Inorganic nitrates or nitrites.
(ii) Organic compounds prepared by bacteria from atmospheric nitrogen.
86.
In the human alimentary canal, name the
site of the complete digestion of various components of food. Explain the process
of digestion. 3
Answer: In the small intestine, complete digestion
of various components of food takes place. The process of digestion of food in the mouth, stomach and small intestine in the human body are as follows:
Mouth: Digestion of food begins in the mouth. Saliva present in the mouth contains a digestive enzyme called salivary amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar.
Stomach: Stomach stores and mixes the food received from the oesophagus with gastric juices. The main components of gastric juice are hydrochloric acid, mucus and pepsinogen.
Hydrochloric acid dissolves bits of food and creates an acidic medium. In this medium, pepsinogen is converted to pepsin which is a protein-digesting enzyme. Mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of HCl.
Small Intestine: Small intestine is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Small intestine produces intestinal juice from the glands present in its wall. The intestinal juice helps in further digestion of food. The small intestine also obtains digestive juices from liver and pancreas that helps in mixing of food.
The liver produces bile juice that causes an emulsification of fats and the pancreas produces pancreatic juice for digesting proteins and emulsified fats. This digested food is finally absorbed through the intestinal walls.
Mouth: Digestion of food begins in the mouth. Saliva present in the mouth contains a digestive enzyme called salivary amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar.
Stomach: Stomach stores and mixes the food received from the oesophagus with gastric juices. The main components of gastric juice are hydrochloric acid, mucus and pepsinogen.
Hydrochloric acid dissolves bits of food and creates an acidic medium. In this medium, pepsinogen is converted to pepsin which is a protein-digesting enzyme. Mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of HCl.
Small Intestine: Small intestine is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Small intestine produces intestinal juice from the glands present in its wall. The intestinal juice helps in further digestion of food. The small intestine also obtains digestive juices from liver and pancreas that helps in mixing of food.
The liver produces bile juice that causes an emulsification of fats and the pancreas produces pancreatic juice for digesting proteins and emulsified fats. This digested food is finally absorbed through the intestinal walls.
87.
(a) What is the role of HCl in our
stomach? 3
(b) What is the emulsification of fats?
(c) Which protein-digesting enzyme is present in pancreatic juice?
(b) What is the emulsification of fats?
(c) Which protein-digesting enzyme is present in pancreatic juice?
Answer:
(a) (i) It sterilises food by killing
pathogens and other microbes.
(ii) It has a pH of 2, which is perfect for entyaus such as pepsin to break down proteins as effectively as possible.
(iii) Helps emulsify food (digestion of protein and stimulates the pancreas to produce digestive enzymes and bile) and protects against harmful bacteria
(b) Breakdown of large globule fats into smaller fats droplets is known as emulsification.
(c) Trypsin is the enzyme secreted by the pancreas which aids in the digestion of proteins.
(ii) It has a pH of 2, which is perfect for entyaus such as pepsin to break down proteins as effectively as possible.
(iii) Helps emulsify food (digestion of protein and stimulates the pancreas to produce digestive enzymes and bile) and protects against harmful bacteria
(b) Breakdown of large globule fats into smaller fats droplets is known as emulsification.
(c) Trypsin is the enzyme secreted by the pancreas which aids in the digestion of proteins.
88.
Explain the process of breakdown of
glucose in a cell 3
(a) in the presence of oxygen,
(b) in the absence of oxygen.
(a) in the presence of oxygen,
(b) in the absence of oxygen.
Answer:
The process of breakdown of glucose in a cell
are as follows:
The first step in the breakdown of glucose
both in the presence of O2 and in absence of O2 is
same. In this step, glucose is broken down into pyruvate.
(a) In the presence of O2: In the presence of O2, pyruvate is converted into CO2 and water. The energy released during aerobic respiration is much greater than that released during anaerobic respiration.
(b) In the absence of O2: In absence of O2 in yeast, pyruvate is converted into ethanol and CO2 and the process is called fermentation. In the absence of O2, in our muscle cells, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid. The build-up of lactic acid in muscle cells causes cramps.
(a) In the presence of O2: In the presence of O2, pyruvate is converted into CO2 and water. The energy released during aerobic respiration is much greater than that released during anaerobic respiration.
(b) In the absence of O2: In absence of O2 in yeast, pyruvate is converted into ethanol and CO2 and the process is called fermentation. In the absence of O2, in our muscle cells, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid. The build-up of lactic acid in muscle cells causes cramps.
89.
(a) “The breathing cycle is rhythmic
whereas the exchange of gases is a continuous process”. Justify this statement. 3
(b) What happens if conducting tubes of the circulatory system develops a leak? State in brief, how could this be avoided?
(c) How the opening and closing of stomata takes place?
(b) What happens if conducting tubes of the circulatory system develops a leak? State in brief, how could this be avoided?
(c) How the opening and closing of stomata takes place?
Answer:
(a) Even though the breathing cycle is
rhythmic, the lungs always contain a residual volume of air so that absorption
of O2 and release of CO2 becomes continuous.
(b) The circulatory system will become inefficient if it develops a leak. This could be avoided by maintaining normal blood pressure.
(c) When water flows into the guard cells, the guard cells swell and the stomatal pore opens up. The guard cells shrink when water moves out and the stomatal pore closes.
(b) The circulatory system will become inefficient if it develops a leak. This could be avoided by maintaining normal blood pressure.
(c) When water flows into the guard cells, the guard cells swell and the stomatal pore opens up. The guard cells shrink when water moves out and the stomatal pore closes.
90. In single-celled organisms, diffusion is sufficient to meet all their
requirements of food, exchange of gases or removal of wastes but it is not in
case of multicellular organisms. Explain the reason for this difference. 3
Answer: In
case of a single-celled organism, the entire surface of the organism is in
contact with the environment and hence no specific organ for taking in food,
exchange of gases or removal of waste may be needed. In the case of a multicellular
organism, the body size of the organism is large. Hence all the cells are not in
direct contact with the surrounding environment. Thus, simple diffusion will
not meet the requirements of the cells.
91.
(a) State three common features of
respiratory organs of animals.
(b) Write two points of difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. 3
(b) Write two points of difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. 3
Answer:
(a) (i) Respiration is the process of gaseous
exchange where CO2 is given out and O2 is taken
in from the air.
(ii) The animal has respiration organs like lungs, gills skin, tracheae.
(iii) Respiration helps blood to become oxygenated that helps food to be carried to different parts of the body.
(b) The difference between aerobic & anaerobic respiration:
(ii) The animal has respiration organs like lungs, gills skin, tracheae.
(iii) Respiration helps blood to become oxygenated that helps food to be carried to different parts of the body.
(b) The difference between aerobic & anaerobic respiration:
92.
(a) Name two different ways in which
glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms. 3
(b) Write any two differences between the two ways of oxidation of glucose in organisms.
(b) Write any two differences between the two ways of oxidation of glucose in organisms.
Answer: (a) The two different ways in which glucose is
oxidised to provide energy in various organisms are as follows:
The first set of the breakdown of glucose (six-carbon molecules) takes place in the
cytoplasm of cells of all organisms. This process yields a three-carbon
molecule compound called pyruvate. Further breakdown of pyruvate takes place
in different manners in different organisms.
(i) Anaerobic respiration which takes place in absence of oxygen, e.g. in yeast
during fermentation. In this case, pyruvate is converted into ethanol and
carbon dioxide.
(ii) Aerobic respiration, in which breakdown of pyruvate takes place in presence of oxygen to give rise to three molecules of carbon dioxide and water.
(b) The two differences between the two ways of oxidation of glucose in organisms are as follows:
(ii) Aerobic respiration, in which breakdown of pyruvate takes place in presence of oxygen to give rise to three molecules of carbon dioxide and water.
(b) The two differences between the two ways of oxidation of glucose in organisms are as follows:
93.
(a) Describe the mechanism of breathing
in human beings.
(b) (i) Under normal conditions, what is the rate of breathing per minute?
(ii) Why does the rate of breathing increase by 20 to 25 times during vigorous exercise? 3
(b) (i) Under normal conditions, what is the rate of breathing per minute?
(ii) Why does the rate of breathing increase by 20 to 25 times during vigorous exercise? 3
Answer:
(a) Mechanism of breathing in Human: Breathing
is a complex mechanical process involving muscular movement that alters the volume of the thoracic cavity and thereby that of the lung.
• Breathing occurs involuntarily but its rate is controlled by the respiratory centre of the brain.
• The space of the thoracic cavity increases or decreases by outward and inward movements of the ribs caused by external intercostal and internal intercostal muscles.
• This action is also assisted by the contraction and expansion of the diaphragm.
• The floor of the thoracic cavity is completely closed by the diaphragm. It is a thin muscular septum separating the abdominal and thoracic cavities.
• Inspiration or inhalation is concerned with the taking in of atmospheric air or oxygen into the thoracic cavity.
• Expiration or exhalation is concerned with the expelling of carbon dioxide from the lungs. It takes place when the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases and the pressure of the contained air in the thoracic cavity increases.
(b) (i) Under normal conditions, the rate of breathing is 12 to 18 times per minute.
(ii) The rate of breathing during vigorous exercise increases by about 20 to 25 times per minute. It is because, during vigorous exercise, the demand for oxygen increases. Breathing occurs involuntarily but its rate is controlled by the respiratory centre of the brain.
• Breathing occurs involuntarily but its rate is controlled by the respiratory centre of the brain.
• The space of the thoracic cavity increases or decreases by outward and inward movements of the ribs caused by external intercostal and internal intercostal muscles.
• This action is also assisted by the contraction and expansion of the diaphragm.
• The floor of the thoracic cavity is completely closed by the diaphragm. It is a thin muscular septum separating the abdominal and thoracic cavities.
• Inspiration or inhalation is concerned with the taking in of atmospheric air or oxygen into the thoracic cavity.
• Expiration or exhalation is concerned with the expelling of carbon dioxide from the lungs. It takes place when the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases and the pressure of the contained air in the thoracic cavity increases.
(b) (i) Under normal conditions, the rate of breathing is 12 to 18 times per minute.
(ii) The rate of breathing during vigorous exercise increases by about 20 to 25 times per minute. It is because, during vigorous exercise, the demand for oxygen increases. Breathing occurs involuntarily but its rate is controlled by the respiratory centre of the brain.
94.
Explain the process by which inhalation
occurs during breathing in human beings. 3
Answer: Inhalation or inspiration is the process by which air is brought into the lungs during breathing in human
beings. It involves the following steps:
(i) The external intercostal muscles contract causing ribs to pull out and chest cavity to expand.
(ii) Diaphragm contracts and is brought down a little. This also expands the chest cavity.
(iii) There is a contraction of the abdominal muscles. The expansion of the chest cavity creates a partial vacuum and atmospheric air rushes the lung.
(i) The external intercostal muscles contract causing ribs to pull out and chest cavity to expand.
(ii) Diaphragm contracts and is brought down a little. This also expands the chest cavity.
(iii) There is a contraction of the abdominal muscles. The expansion of the chest cavity creates a partial vacuum and atmospheric air rushes the lung.
 |
95. How does a gaseous exchange take place in Amoeba? 3
Answer: Gaseous
exchange in Amoeba: Amoeba has no special respiratory pigment. But there is a
free exchange of gases that takes place by diffusion or osmosis through the
general body surface, which is permeable to the respiratory gases dissolved in
water. Oxygen constantly diffuses in the cytoplasm for its concentration in
water is always higher than in the cytoplasm. The oxygen used is not obtained
from the water molecule. It is free oxygen dissolved in water from the atmosphere or
produced as a by-product during the process of photosynthesis by the aquatic
plants. Carbon dioxide diffuses out as it is always in a higher concentration
within the body of Amoeba than in the surrounding water.
96. What are stomata and lenticels? What is their role in respiration? 3
Answer: Stomata or stoma
is a pore, large numbers of which are present in the epidermis of leaves and
young shoots. Each stoma is bordered by two semicircular guard cells. Stomata
functions in the gaseous exchange between the plant and the atmosphere.
Lenticel is any of the raised pores in the stems of
woody plants. The pore is formed by the cork cambium, which at certain points
produce a loose bulky form of cork that pushes through the outer tissues to
create the lenticel. Lenticel function in gas exchange between the atmosphere
and the internal tissues.
97. How does a gaseous exchange take place in fish? 3
Answer: Aquatic animals
like fish use gills as their respiratory organ. Respiration through gills is
known as branchial respiration. The blood flowing in the capillaries of gills
absorb oxygen and gives carbon dioxide to the water passing over them by
diffusion through the thin epithelium.
98.Draw a diagram of the human respiratory system
and label on it: 3
(a) Diaphragm (b) Larynx
(a) Diaphragm (b) Larynx
Answer:
99. In mammals and birds, why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and
de-oxygenated blood? 3
Answer: Mammals and birds
are warm-blooded animals. This means they can control their body temperature
and they need not depend on the environment for body temperature regulation.
Because of this birds and mammals need optimum oxidation of glucose which is
possible with a good supply of oxygen. Four chambered heart in birds and mammals
ensures that deoxygenated blood does not get mixed with oxygenated blood.
100. Mention the three kinds of cells present in the blood. Write one function of
each. 3
Answer: Blood is made up
of plasma and corpuscles. Three kinds of corpuscles are: WBC, RBC and Blood
platelets Red Blood corpuscles (RBC) are small, biconvex cells that contain
haemoglobin to transport O2 from the lungs to the body cells
and CO2 from body cells to the lungs. White blood cells (WBC) the main function is the defence of the body against diseases and other infection.
Blood platelets are responsible for the clotting of blood during injuries.
Life process
Life process
101. List the three kinds of blood
vessels of the human circulatory system and write their functions in tabular form. 3
Answer: Three types of
blood vessels in the human circulatory system are -Arteries, Veins and Capillaries.
Their functions are tabulated below:
102. Draw a diagram of the front view of the human heart and label any six parts including at least two, that are concerned
with arterial blood supply to the heart muscles. 3
Answer:
103.
(a) Label any 4 parts in the given diagram.
3
(b) What are the two functions represented in this diagram?
(b) What are the two functions represented in this diagram?
Answer:
(a) 1. Pulmonary artery to lungs
2. Lung capillaries 3. A pulmonary vein from lungs 4. Aorta to body 5.
Capillaries in body organs 6. Vena cava from the body. (any four)
(b) The two functions represented are :
(i) Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide
(ii) Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
(b) The two functions represented are :
(i) Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide
(ii) Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
104.
Write one function of each of the following components of the transport system
in human beings: 3
(a) Blood vessels (b) Lymph (c) Heart
(a) Blood vessels (b) Lymph (c) Heart
Answer: Function
of the following components of the transport system in human beings are as
follows:
(a) Blood vessels: There are three types of blood vessels of different sizes involved in blood circulation viz. arteries, veins and capillaries, which are all connected to form a continuous closed system.
(b) Lymph: It carries digested and absorbed fat from intestine and drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood.
(c) Heart: It is a pumping organ that receives blood from the veins and pumps it into the arteries.
(a) Blood vessels: There are three types of blood vessels of different sizes involved in blood circulation viz. arteries, veins and capillaries, which are all connected to form a continuous closed system.
(b) Lymph: It carries digested and absorbed fat from intestine and drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood.
(c) Heart: It is a pumping organ that receives blood from the veins and pumps it into the arteries.
105.
What is blood pressure? How it is measured ? Give one difference between
systolic pressure and diastolic pressure.
3
Answer: Blood
Pressure: It is the force that blood exerts against the wall of a vessel. This
pressure is much greater in arteries than in veins. It is measured by using an
instrument called a sphygmomanometer.
The pressure of blood inside the artery during contraction or ventricular systole is called systolic pressure and pressure in the artery during relaxation or ventricular diastole is called diastolic pressure. The normal systolic pressure is about 120 mm of Hg and diastolic pressure is 80 mm of Hg.
The pressure of blood inside the artery during contraction or ventricular systole is called systolic pressure and pressure in the artery during relaxation or ventricular diastole is called diastolic pressure. The normal systolic pressure is about 120 mm of Hg and diastolic pressure is 80 mm of Hg.
106.
State the role of the following in the human digestive system: 3
(a) Digestive enzymes (b) Hydrochloric acid (c) Villi
(a) Digestive enzymes (b) Hydrochloric acid (c) Villi
Answer:
(a)
Digestive enzymes digest the food we eat.
(b) Hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium to facilitate the action of enzyme pepsin.
(c) Villi increase the surface area inside the small intestine to facilitate absorption of food.
(b) Hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium to facilitate the action of enzyme pepsin.
(c) Villi increase the surface area inside the small intestine to facilitate absorption of food.
107.
Describe in brief the function of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and
urethra. 3
Answer: Functions
of Kidneys
It removes the nitrogenous wastes such as urea and excess water from the blood. It regulates the osmotic pressure/water balance/pH of the blood.
Functions of Ureters
Urine formed in each kidney is carried by the long tube called ureter to the urinary bladder. Some amount of glucose, amino acid, salt and a major amount of water are reabsorbed in the ureter.
Functions of Urinary bladder
It acts as a reservoir that stores urine before being discharged to the outside.
Functions of Urethra
Urine is passed out from the body through the urethra.
It removes the nitrogenous wastes such as urea and excess water from the blood. It regulates the osmotic pressure/water balance/pH of the blood.
Functions of Ureters
Urine formed in each kidney is carried by the long tube called ureter to the urinary bladder. Some amount of glucose, amino acid, salt and a major amount of water are reabsorbed in the ureter.
Functions of Urinary bladder
It acts as a reservoir that stores urine before being discharged to the outside.
Functions of Urethra
Urine is passed out from the body through the urethra.
108.
Draw a diagram of the human excretory system and label kidneys, ureters on it. 3
Answer:
109.
Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons. 5
Answer: Structure
of a Nephron: A nephron is made up of
(i) A globular double-walled Bowman’s capsule around a cluster of capillaries or glomerulus. The blood enters into glomerulus through afferent arteriole of the renal artery and leaves it through the efferent arteriole.
(ii) Tubule surrounded by blood capillaries. It consists of:
(a) Proximal convoluted portion.
(b) The loop of Henle with descending and ascending limbs, and
(c) A distal convoluted part.
The nephron empties into a collecting duct. The tubule is connected with collecting duct at one end and a cup-shaped structure, i.e. the Bowman’s the capsule at the other end.
The functioning of Nephron:
Urine is formed by three processes–glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion.
(i) Filtration: Filtration of blood takes place in Bowman’s capsule from the capillaries of the glomerulus. The filtrate passes into the tubular part of the nephron. This filtrate contains glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid, salts and a major amount of water.
(ii) Reabsorption: As the filtrate flows along the tubule useful substances such as glucose, amino acids, salts and water are selectively reabsorbed into the blood by capillaries surrounding the nephron tubule.
(iii) Tubular Secretion: The filtrate which remains after reabsorption is called urine. Urine is collected from nephrons by the collecting duct to carry it to the ureter. The secretion of H+ helps to regulate the pH of the blood.
(i) A globular double-walled Bowman’s capsule around a cluster of capillaries or glomerulus. The blood enters into glomerulus through afferent arteriole of the renal artery and leaves it through the efferent arteriole.
(ii) Tubule surrounded by blood capillaries. It consists of:
(a) Proximal convoluted portion.
(b) The loop of Henle with descending and ascending limbs, and
(c) A distal convoluted part.
The nephron empties into a collecting duct. The tubule is connected with collecting duct at one end and a cup-shaped structure, i.e. the Bowman’s the capsule at the other end.
The functioning of Nephron:
Urine is formed by three processes–glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion.
(i) Filtration: Filtration of blood takes place in Bowman’s capsule from the capillaries of the glomerulus. The filtrate passes into the tubular part of the nephron. This filtrate contains glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid, salts and a major amount of water.
(ii) Reabsorption: As the filtrate flows along the tubule useful substances such as glucose, amino acids, salts and water are selectively reabsorbed into the blood by capillaries surrounding the nephron tubule.
(iii) Tubular Secretion: The filtrate which remains after reabsorption is called urine. Urine is collected from nephrons by the collecting duct to carry it to the ureter. The secretion of H+ helps to regulate the pH of the blood.
110.
(a)
Draw a diagram to show open stomatal pore and label on it:
(i) guard cells (ii) chloroplast
(b) State two functions of stomata.
(c) How do guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pore? 3
(i) guard cells (ii) chloroplast
(b) State two functions of stomata.
(c) How do guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pore? 3
Answer: (a)
(b) Two
functions of stomata are:
(i) Exchange of gases between the plant and the atmosphere takes place through stomata.
(ii) Transpiration in plants takes place through stomata.
(c) Opening and Closing of Stomatal Pore. The opening and closing of the pore is a function of
the guard cells. The guard cells swell when water flows into them causing the stomatal pore
to open. Similarly, the pore closes if the guard cells shrink. As a large amount of water is lost
through these stomata, the plant closes these pores when it does not require carbon dioxide
for photosynthesis.
(i) Exchange of gases between the plant and the atmosphere takes place through stomata.
(ii) Transpiration in plants takes place through stomata.
(c) Opening and Closing of Stomatal Pore. The opening and closing of the pore is a function of
the guard cells. The guard cells swell when water flows into them causing the stomatal pore
to open. Similarly, the pore closes if the guard cells shrink. As a large amount of water is lost
through these stomata, the plant closes these pores when it does not require carbon dioxide
for photosynthesis.
111.
(a) Leaves of a healthy potted plant
were coated with vaseline to block the stomata. Will this plant remain healthy
for long? State three reasons for your answer.
(b) State any two differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition. 3
(b) State any two differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition. 3
Answer: (a) No, this the plant will not remain healthy for long.
The plant will begin to die because
(i) The gaseous exchange will not take place.
(ii) No absorption of CO2, hence no photosynthesis.
(iii) Transpiration will not occur; hence no transport of water.
The plant will begin to die because
(i) The gaseous exchange will not take place.
(ii) No absorption of CO2, hence no photosynthesis.
(iii) Transpiration will not occur; hence no transport of water.
(b) Differences
Autotrophic nutrition
|
Heterotrophic nutrition
|
(i) In this, the organisms make their food from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
|
(i) In this, the organisms derive their food or nutrients from other living organisms.
|
(ii) All green plants are autotrophic and use light as a source of energy for synthesis.
|
(ii) The energy is derived from the intake and digestion of organic substances.
|
112.
(a) List the three events that occur
during the process of photosynthesis. Explain the role of stomata in this
process.
(b) Describe an experiment to show that “sunlight is essential for photosynthesis.” 5
(b) Describe an experiment to show that “sunlight is essential for photosynthesis.” 5
Answer:
(a) The three events that occur during the
process of photosynthesis are :
(i) Absorption of light energy by the green pigment chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy into chemical energy and the splitting of water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen.
(iii) Reduction of carbon dioxide into carbohydrate.
Role of Stomata
Stomata are tiny pores present on the surface of leaves. They are also present on the surface of young stems and roots, stomata are mainly engaged in the exchange of gases (entry of CO2 and release of O2) associated with photosynthesis. The plant closes the stomata when it does not need CO2 for photosynthesis.
(b) Sunlight is essential for Photosynthesis: A healthy green potted plant is placed in a dark room for 1-2 days. This is done to ensure that the plant consumes all its reserve food and the leaves do not contain any starch. Both sides of a green leaf is covered with two uniform pieces of black paper and then fix the cover in position with two paper clips.
Now, the plant is exposed to bright light. After a few hours, the leaf is removed and it is decolourised with alcohol. Now, the presence of food (starch) is tested by putting iodine solution on the leaf. It can be observed that the covered portion of the leaf does not show any presence of starch (food).
This is because plants store the food prepared by the process of photosynthesis as starch. Starch reacts with an iodine solution to give blue-black colour. In this experiment, only those portions of the leaf that were exposed to light could photosynthesise. Hence, the uncovered portion of the leaf gives blue-black colour when tested with iodine. So, the covered portion does not change its colour when treated with iodine solution.
Thus, it can be concluded that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis.
(i) Absorption of light energy by the green pigment chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy into chemical energy and the splitting of water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen.
(iii) Reduction of carbon dioxide into carbohydrate.
Role of Stomata
Stomata are tiny pores present on the surface of leaves. They are also present on the surface of young stems and roots, stomata are mainly engaged in the exchange of gases (entry of CO2 and release of O2) associated with photosynthesis. The plant closes the stomata when it does not need CO2 for photosynthesis.
(b) Sunlight is essential for Photosynthesis: A healthy green potted plant is placed in a dark room for 1-2 days. This is done to ensure that the plant consumes all its reserve food and the leaves do not contain any starch. Both sides of a green leaf is covered with two uniform pieces of black paper and then fix the cover in position with two paper clips.
Now, the plant is exposed to bright light. After a few hours, the leaf is removed and it is decolourised with alcohol. Now, the presence of food (starch) is tested by putting iodine solution on the leaf. It can be observed that the covered portion of the leaf does not show any presence of starch (food).
This is because plants store the food prepared by the process of photosynthesis as starch. Starch reacts with an iodine solution to give blue-black colour. In this experiment, only those portions of the leaf that were exposed to light could photosynthesise. Hence, the uncovered portion of the leaf gives blue-black colour when tested with iodine. So, the covered portion does not change its colour when treated with iodine solution.
Thus, it can be concluded that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis.
113. Explain the process of ‘photosynthesis’ in plants. List four factors
which influence this process and describe how each of them affects the rate of
the photosynthesis process. 5
Answer: ‘Photosynthesis’ is a process in which
green plants use sunlight, chlorophyll, CO2 and water to
synthesise organic food in the form of carbohydrates.
It occurs in two stages:
(i) Light reaction: During this reaction, ATP and NADPH are generated. this step is light-dependent.
(ii) Dark reaction: It is not dependent on light. During this reaction, CO2 is reduced to carbohydrate.
Source of energy is ATP and NADPH.
(i) Light reaction: During this reaction, ATP and NADPH are generated. this step is light-dependent.
(ii) Dark reaction: It is not dependent on light. During this reaction, CO2 is reduced to carbohydrate.
Source of energy is ATP and NADPH.
114.
(a) Explain how does the exchange of
gases occur in plants across the surface of stems, roots and leaves.
(b) How are water and minerals transported in plants? 5
(b) How are water and minerals transported in plants? 5
Answer: (a) In plants there are tiny pores
called stomata on leaves and lenticels in the stem which facilitate the exchange of
gases. Carbon dioxide is taken in and oxygen is given out {during photosynthesis}
and vice versa during respiration.
(b) Water and minerals are transported within the plant by the Xylem vessels (mainly in an upward direction); these are part of the vascular system which also includes Phloem vessels. Phloem transports the products of photosynthesis within the plant, to all parts like the stem, roots, fruits etc. in all directions.
(b) Water and minerals are transported within the plant by the Xylem vessels (mainly in an upward direction); these are part of the vascular system which also includes Phloem vessels. Phloem transports the products of photosynthesis within the plant, to all parts like the stem, roots, fruits etc. in all directions.
115.
(a) Draw a diagram to show the
nutrition in Amoeba and label the parts used for this purpose. Mention any
other purpose served by this part other than nutrition.
(b) Name the glands associated with digestion of starch in the human digestive tract and mention their role.
(c) How is the required pH maintained in the stomach and small intestine? 5
(b) Name the glands associated with digestion of starch in the human digestive tract and mention their role.
(c) How is the required pH maintained in the stomach and small intestine? 5
Answer:
(a)
Pseudopodia serves the purpose of locomotion apart
from nutrition.
(b) The salivary gland is associated with digestion of starch in the human digestive tract. It secretes saliva with the help of enzyme salivary amylase which converts starch into maltose (sugar).
(c) Gastric glands present on the walls of the stomach release HCl acid. HCl creates an acidic medium, which facilitates the action of the enzyme pepsin. Bile juice from liver makes the food alkaline in the small intestine for the pancreatic enzymes to act.
(b) The salivary gland is associated with digestion of starch in the human digestive tract. It secretes saliva with the help of enzyme salivary amylase which converts starch into maltose (sugar).
(c) Gastric glands present on the walls of the stomach release HCl acid. HCl creates an acidic medium, which facilitates the action of the enzyme pepsin. Bile juice from liver makes the food alkaline in the small intestine for the pancreatic enzymes to act.
116.
(a) Draw a diagram depicting Human
Alimentary Canal and label on it: Gall bladder, Liver and Pancreas. 5
(b) State the roles of Liver and Pancreas.
(c) Name the organ which performs the following functions in humans:
(i) Absorption of digested food
(ii) Absorption of water.
(b) State the roles of Liver and Pancreas.
(c) Name the organ which performs the following functions in humans:
(i) Absorption of digested food
(ii) Absorption of water.
Answer:
(a)
(b) Liver: It secretes bile juice which breaks
down fats into fat globules. Pancreas: It secretes pancreatic juice which
contains protein-digesting and starch digesting enzymes.
(c) The organ which performs the following functions in humans are as follows:
(i) Absorption of digested food – Ileum of the small intestine.
(ii) Absorption of water – Large intestine.
(c) The organ which performs the following functions in humans are as follows:
(i) Absorption of digested food – Ileum of the small intestine.
(ii) Absorption of water – Large intestine.
117.
Explain the process of digestion of
food in the mouth, stomach and small intestine in the human body. 5
Answer: The process of digestion of food in the mouth, stomach and small intestine in the human body are as follows:
Mouth: Digestion of food begins in the mouth. Saliva present in the mouth contains a digestive enzyme, called salivary amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar. Stomach: Stomach stores and mixes the food received from the oesophagus with gastric juices. The main components of gastric juice are hydrochloric acid, mucus and pepsinogen.
Hydrochloric acid dissolves bits of food and creates an acidic medium. In this medium, pepsinogen is converted to pepsin which is a protein-digesting enzyme. Mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of HCl.
Small Intestine: Small intestine is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Small intestine produces intestinal juice from the glands present in its wall. The intestinal juice helps in further digestion of food. The small intestine also obtains digestive juices from liver and pancreas that helps in mixing of food.
The liver produces bile juice that causes an emulsification of fats and the pancreas produces pancreatic juice for digesting proteins and emulsified fats. This digested food is finally absorbed through the intestinal walls.
Mouth: Digestion of food begins in the mouth. Saliva present in the mouth contains a digestive enzyme, called salivary amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar. Stomach: Stomach stores and mixes the food received from the oesophagus with gastric juices. The main components of gastric juice are hydrochloric acid, mucus and pepsinogen.
Hydrochloric acid dissolves bits of food and creates an acidic medium. In this medium, pepsinogen is converted to pepsin which is a protein-digesting enzyme. Mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of HCl.
Small Intestine: Small intestine is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Small intestine produces intestinal juice from the glands present in its wall. The intestinal juice helps in further digestion of food. The small intestine also obtains digestive juices from liver and pancreas that helps in mixing of food.
The liver produces bile juice that causes an emulsification of fats and the pancreas produces pancreatic juice for digesting proteins and emulsified fats. This digested food is finally absorbed through the intestinal walls.
118. (a) Complete the glucose breakdown pathway in
case of aerobic respiration by filling the blanks.
(b) Name the molecule in the cell which stores the
energy produced at the end of the pathway.
(c) Why do we get cramps during the vigorous muscular activity? 5
(c) Why do we get cramps during the vigorous muscular activity? 5
Answer:
(a) (1) Pyruvate (3 carbon molecules) (2) Energy (3)
Presence of oxygen (4) In Mitochondria (5) Carbon dioxide (6) Water
(b) ATP
(c) Lactic acid accumulation, in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic respiration)cause cramps.
(b) ATP
(c) Lactic acid accumulation, in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic respiration)cause cramps.
119.
(a) Draw a labelled diagram of the
respiratory system of human beings with the diaphragm at the end of expiration.
(b) List four conditions required for efficient gas exchange in an organism. 5
(b) List four conditions required for efficient gas exchange in an organism. 5
Answer:
(a)
(b) The conditions required for efficient gas
exchange in an organism are that the membrane should be extensive, thin, highly
vascularised and easily permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide.
120. (a) Draw a schematic representation of transport and exchange of oxygen
and carbon dioxide during transportation of blood in human beings and label on
it: Lung capillaries, Pulmonary artery to lungs, Aorta to the body, Pulmonary veins
from the lungs.
(b) What is the advantage of separate channels in mammals and birds for oxygenated and deoxygenated blood? 5
(b) What is the advantage of separate channels in mammals and birds for oxygenated and deoxygenated blood? 5
Answer:
(a)
(b) It is necessary to separate oxygenated and
deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds because they need high energy and a large amount of oxygen. The separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
provides high oxygen supply to the organs.
121.
(a) Draw a sectional view of the human
heart and label on it – Aorta, Right ventricle and Pulmonary veins.
(b) State the functions of the following components of the transport system:
(b) State the functions of the following components of the transport system:
(i) Blood (ii) Lymph 5
Answer:
(a)
(b) The functions of the following components
of the transport system are :
(i) Blood:
• Oxygen is transported to the tissues of the body for the purpose of respiration.
• Carbon dioxide is transported to the lungs by the blood plasma.
• The digested and absorbed nutrients are transported to the tissues.
• Nitrogenous wastes are transported to the kidneys.
• The blood regulates the body temperature.
• It maintains the pH of the body tissues.
• It transports various hormones from one region to another and bring about the coordination.
• It maintains water balance to a constant level.
• The lymphocytes produce antibodies against the invading antigens and protects from diseases.
• Blood helps in rapid healing of wounds by forming a clot at the site of injury.
(ii) Lymph:
• It carries digested and absorbed fat from the intestine and drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood.
• It protects the body by killing the germs drained out of the body tissues with the help of lymphocytes contained in the lymph nodes.
(i) Blood:
• Oxygen is transported to the tissues of the body for the purpose of respiration.
• Carbon dioxide is transported to the lungs by the blood plasma.
• The digested and absorbed nutrients are transported to the tissues.
• Nitrogenous wastes are transported to the kidneys.
• The blood regulates the body temperature.
• It maintains the pH of the body tissues.
• It transports various hormones from one region to another and bring about the coordination.
• It maintains water balance to a constant level.
• The lymphocytes produce antibodies against the invading antigens and protects from diseases.
• Blood helps in rapid healing of wounds by forming a clot at the site of injury.
(ii) Lymph:
• It carries digested and absorbed fat from the intestine and drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood.
• It protects the body by killing the germs drained out of the body tissues with the help of lymphocytes contained in the lymph nodes.
122. (a) Name the blood vessel
that brings oxygenated blood to the human heart.
(b) Which chamber of the human heart receives oxygenated blood?
(c) Explain how oxygenated blood from this chamber is sent to all parts of the body. 5
(b) Which chamber of the human heart receives oxygenated blood?
(c) Explain how oxygenated blood from this chamber is sent to all parts of the body. 5
Answer:
(a) The pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood
to the human heart.
(b) The left auricle of the human heart receives oxygenated blood.
(c) (i) When oxygenated blood comes into the left atrium, it contracts and pours blood into the left ventricle.
(ii) The left ventricle contracts and the oxygenated blood from here is distributed to all parts of the body through the aorta.
(b) The left auricle of the human heart receives oxygenated blood.
(c) (i) When oxygenated blood comes into the left atrium, it contracts and pours blood into the left ventricle.
(ii) The left ventricle contracts and the oxygenated blood from here is distributed to all parts of the body through the aorta.
123.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of the excretory
system of human beings and label the following:
(i) Kidney (ii) Ureter (iii) Urinary Bladder (iv) Urethra
(b) How is urine produced?
(c) Name two excretory products other than O2 and CO2 in plants. 5
(i) Kidney (ii) Ureter (iii) Urinary Bladder (iv) Urethra
(b) How is urine produced?
(c) Name two excretory products other than O2 and CO2 in plants. 5
Answer:
(a)
(b) Mechanism of Urine Formation. Urine is formed in the kidneys. There
are numerous excretory units called nephrons and each nephron is a very thin
thread-like structure with its one end bearing a cup-shaped structure known as
Bowman’s capsule. A thin network of blood vessels known as glomerulus is
present in the Bowman’s capsule, which consists of afferent and efferent
arterioles. Urine is formed in two stages called filtration and reabsorption
(Fig.). In the filtration, blood is filtered into kidney tubules to form a clear
fluid containing the waste substance urea, and many useful substances like
glucose and amino acids. The filtration occurs in the glomeruli. The useful
substances are reabsorbed from the filtrate back into the blood leaving only
urea and other substances in the kidney tubules.
124.
(a) Explain how does the exchange of
gases occur in plants across the surface of stems, roots and leaves.
(b) How are water and minerals transported in plants? 5
(b) How are water and minerals transported in plants? 5
Answer:
(a) In plants, there are tiny pores called stomata
on leaves and lenticels in the stem which facilitate the exchange of gases. CO2 is
taken in and O2 given out (during photosynthesis) and
vice-versa during respiration.
(b) Mechanism of Transport of Water and Minerals in a Plant
• The vessels and tracheids of roots, stems and leaves in xylem tissue are interconnected to form a continuous system of water-conducting channels reaching all parts of the plant.
• The cells of the roots in contact with the soil actively take up ions which creates a difference in the ion concentration between the root and the soil.
• Thus, there is a steady movement of water into root xylem from the soil, creating a column of water that is pushed upwards.
• Plant uses another strategy to move water in the xylem upwards to the highest points of the plant body.
• The water which is lost through the stomata is replaced by water from the xylem vessels in the leaf.
• Evaporation of water molecules from the cells of a leaf creates a suction which pulls water from the xylem cells of roots.
• This loss of water is transpiration which helps in the absorption and upward movement of water and minerals dissolved in it from roots to the leaves.
• Transpiration becomes the major driving force in the movement of water in the xylem during the day when the stomata are open.
• This mechanism is also known as a cohesion of water theory or transpiration pull.
(b) Mechanism of Transport of Water and Minerals in a Plant
• The vessels and tracheids of roots, stems and leaves in xylem tissue are interconnected to form a continuous system of water-conducting channels reaching all parts of the plant.
• The cells of the roots in contact with the soil actively take up ions which creates a difference in the ion concentration between the root and the soil.
• Thus, there is a steady movement of water into root xylem from the soil, creating a column of water that is pushed upwards.
• Plant uses another strategy to move water in the xylem upwards to the highest points of the plant body.
• The water which is lost through the stomata is replaced by water from the xylem vessels in the leaf.
• Evaporation of water molecules from the cells of a leaf creates a suction which pulls water from the xylem cells of roots.
• This loss of water is transpiration which helps in the absorption and upward movement of water and minerals dissolved in it from roots to the leaves.
• Transpiration becomes the major driving force in the movement of water in the xylem during the day when the stomata are open.
• This mechanism is also known as a cohesion of water theory or transpiration pull.
125.
(a) Draw the structure of a nephron and
label the following on it: Glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, Renal artery,
Collecting duct.
(b) What happens to glucose that enters the nephron along with filtrate? 5
(b) What happens to glucose that enters the nephron along with filtrate? 5
Answer:
(a)
(b) During excretion in human beings, glucose
which enters the nephron along with filtrate gets reabsorbed by the blood
capillaries surrounding the nephron.
Life process
Life process
126.
Your family has a plot of land in the
city where your father wants to construct a house. The area has few trees which
are very dear to your father. By way of photosynthesis, trees provide oxygen
which is essential for living organisms. Your father, therefore, does not want
to cut the trees. At the same time, he desperately needs a house for his
family. 4
(a) Should your father construct the house after cutting the trees?
(b) How can you compensate for the loss in terms of oxygen supply?
(c) Will simply planting the trees ensure supply of oxygen?
(d) What values are shown by your father?
(a) Should your father construct the house after cutting the trees?
(b) How can you compensate for the loss in terms of oxygen supply?
(c) Will simply planting the trees ensure supply of oxygen?
(d) What values are shown by your father?
Answer:
(a) Yes, he should construct the house by
cutting the minimum numbers of trees.
(b) We will plant equal numbers of trees in a different place to compensate for the loss.
(c) No. We have to water the trees regularly in the initial stage. The trees are also to be maintained
by weeding and also by protecting them from animals in the initial stage.
(d) The value shown is love for nature and concern for the protection of environment.
(b) We will plant equal numbers of trees in a different place to compensate for the loss.
(c) No. We have to water the trees regularly in the initial stage. The trees are also to be maintained
by weeding and also by protecting them from animals in the initial stage.
(d) The value shown is love for nature and concern for the protection of environment.
127.
You were in a party where people were
dancing on the dancing floor. A person on the floor suddenly felt severe pain
on the chest. He also felt dizziness. Some people were mentioning that he might
have a heart attack. 4
(a) What are the causes of a heart attack?
(b) What are the symptoms of a heart attack?
(c) What should you do when you see a person who may have suffered from a heart attack?
(a) What are the causes of a heart attack?
(b) What are the symptoms of a heart attack?
(c) What should you do when you see a person who may have suffered from a heart attack?
Answer:
(a) The main causes of a heart attack are –
high level of cholesterol, hereditary factor, tobacco consumption, obesity,
high blood pressure, stress, inflammatory diseases of arteries, trauma and the disease of heart.
(b) The symptoms of a heart attack are— chest pain, pain on the shoulder, dizziness, shortness of breath, sweating, heartburn and nausea.
(c) I will call an ambulance immediately to take the person to a hospital. The following first aid will be provided to the person—
(i) The person will be made calm.
(ii) His tight clothes will be made little loose to facilitate easy breathing.
(iii) If no pulse is detected, he will be helped in respiration by pumping the chest and by blowing through his mouth. 15 pumps should be followed by 2 artificial respirations.
(b) The symptoms of a heart attack are— chest pain, pain on the shoulder, dizziness, shortness of breath, sweating, heartburn and nausea.
(c) I will call an ambulance immediately to take the person to a hospital. The following first aid will be provided to the person—
(i) The person will be made calm.
(ii) His tight clothes will be made little loose to facilitate easy breathing.
(iii) If no pulse is detected, he will be helped in respiration by pumping the chest and by blowing through his mouth. 15 pumps should be followed by 2 artificial respirations.
128.
You were standing on the roadside when
you saw a family travelling in a car. An ambulance carrying a patient for
dialysis was travelling behind the car. The driver of the car brought his car
to one side of the road and allowed the ambulance to overtake.
(a) What value was shown by the driver?
(b) What is dialysis?
(c) What are the vehicles whom we should give pass while driving? 4
(a) What value was shown by the driver?
(b) What is dialysis?
(c) What are the vehicles whom we should give pass while driving? 4
Answer:
(a) The values showed by the driver were love
for mankind and his driving knowledge.
(b) It is a procedure used on patients whose kidneys have got damaged. In the process, the blood of the patient is allowed to pass through the long cellulose tubes dipped in a tank containing dialysing solution having same ionic concentration as plasma. The waste substances diffuse out of the blood into the tank and the cleaned blood is returned back into the patient through a vein.
(c) We should always give a pass to ambulances, fire brigades and police vehicles.
(b) It is a procedure used on patients whose kidneys have got damaged. In the process, the blood of the patient is allowed to pass through the long cellulose tubes dipped in a tank containing dialysing solution having same ionic concentration as plasma. The waste substances diffuse out of the blood into the tank and the cleaned blood is returned back into the patient through a vein.
(c) We should always give a pass to ambulances, fire brigades and police vehicles.
129.
An organ donation camp was organized by the government in your locality to encourage people for organ donation. But the
camp was not very successful. The camp hardly received any response. 4
(a) What values are possessed by people who wish to donate their organs?
(b) Will organ donation agreement affect the donor?
(c) Why did the organ donation camp fail?
(a) What values are possessed by people who wish to donate their organs?
(b) Will organ donation agreement affect the donor?
(c) Why did the organ donation camp fail?
Answer:
(a) People who donate organ show love for
mankind.
(b) Organ donation agreement does not affect the donor as the organs are removed only after the death of the person.
(c) The organ donation camp failed because people are still not well informed about organ donation.
The government can launch a campaign to make people aware of organ donation.
Life process
(b) Organ donation agreement does not affect the donor as the organs are removed only after the death of the person.
(c) The organ donation camp failed because people are still not well informed about organ donation.
The government can launch a campaign to make people aware of organ donation.
Life process




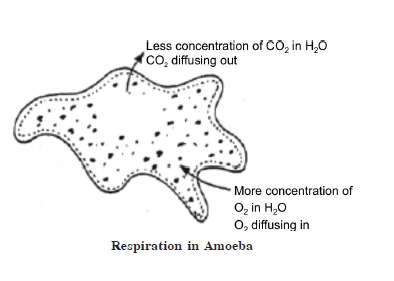


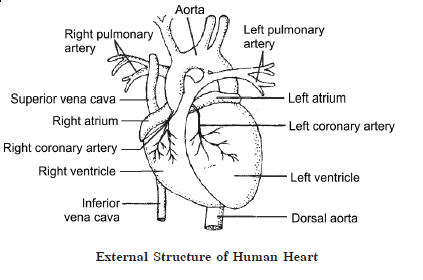







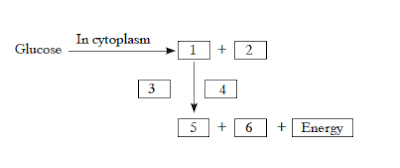
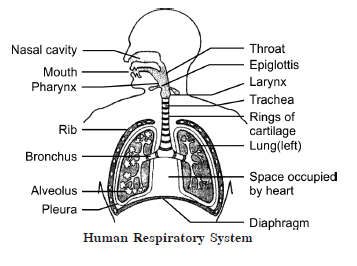



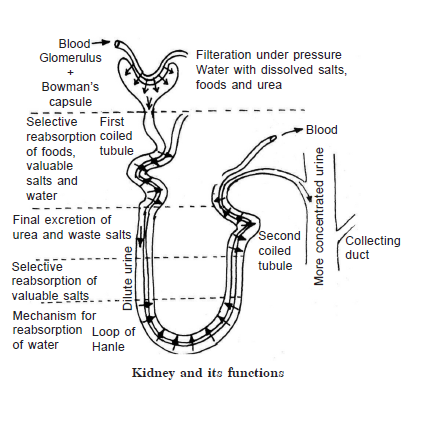











0 comments:
Post a Comment