How
do Organisms Reproduce?
 |
| BIOLOGY |
TEST PAPER
CHAPTER - HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE?
1.
There is a greater possibility for the evolution of a new species in organisms
which reproduce by 1 👇
(a) binary fission (b) budding (c)
fertilisation (d) regeneration
Answer: (c)
2. Which is the most common method of
reproduction in the majority of fungi and bacteria? 1 👇
(a) Budding (b) Spore formation (c) Binary fission (d) Multiple fission
(a) Budding (b) Spore formation (c) Binary fission (d) Multiple fission
Answer: (b)
3. Which of the following is not an artificial
method of vegetative propagation?
(a) Cutting (b) Layering (c) Budding (d) Grafting 1 👇
(a) Cutting (b) Layering (c) Budding (d) Grafting 1 👇
Answer: (c)
4. Many unicellular organisms reproduce by the
process of 1 👇
(a) fission (b) ovulation (c) regeneration (d) non-disjunction
(a) fission (b) ovulation (c) regeneration (d) non-disjunction
Answer: (a)
5. The ability of an organism to develop a whole
body from a broken piece or fragment is called 1 👇
(a) binary fission (b) budding (c) multiple fission (d) regeneration
Answer: (d)
6. Pollen grains are produced by 1 👇
(a) ovary (b) ovule (c) anther (d) corolla
(a) ovary (b) ovule (c) anther (d) corolla
Answer: (c)
7. The fertilisation of a human egg by the sperm
takes place in 1 👇
(a) vagina (b) uterus (c) ovary (d) oviduct
(a) vagina (b) uterus (c) ovary (d) oviduct
Answer: (d)
8. Which of the following is a primary sex organ
in a mammal? 1 👇
(a)
Ovary (b) Vagina (c) Uterus (d) Mammary glands
Answer: (a)
9. The ability to reproduce is lost in a female
after 1 👇
(a) fertilisation (b) menstruation (c) gamete formation (d) menopause
(a) fertilisation (b) menstruation (c) gamete formation (d) menopause
Answer: (d)
10.
When sperm is deposited into the vagina which route does it travel? 1 👇
(a) Vagina → Oviduct → Uterus → Cervix
(b) Vagina → Ovary → Uterus → Oviduct
(c) Vagina → Cervix → Uterus → Oviduct
(d) Vagina → Uterus → Cervix → Oviduct
(a) Vagina → Oviduct → Uterus → Cervix
(b) Vagina → Ovary → Uterus → Oviduct
(c) Vagina → Cervix → Uterus → Oviduct
(d) Vagina → Uterus → Cervix → Oviduct
Answer: (c)
11. In case the ovum does not fertilise, which of
the following events will take place?
(a) Menstruation (b) Pregnancy (c) Implantation (d) Ovulation 1 👇
(a) Menstruation (b) Pregnancy (c) Implantation (d) Ovulation 1 👇
Answer: (a)
12. When the foetus is growing inside the uterus
it needs nutrients. Which part provides these nutrients? 1 👇
(a) Placenta (b) Amniotic sac (c) Oviduct (d) Uterus
(a) Placenta (b) Amniotic sac (c) Oviduct (d) Uterus
Answer: (a)
13. What marks the beginning of the reproductive
life of a woman? 1 👇
(a) Menopause (b) Menarche (c) Fertilisation (d) Ovulation
(a) Menopause (b) Menarche (c) Fertilisation (d) Ovulation
Answer: (b)
14. Where does fertilisation take place? 1 👇
(a) Uterus (b) Vagina (c) Fallopian tube (d) Cervix
(a) Uterus (b) Vagina (c) Fallopian tube (d) Cervix
Answer: (c)
15. A pair of duct arising from testis, which
carry sperms are 1 👇
(a) fallopian tube (b) vas deferens (c) oviduct (d) urethra
(a) fallopian tube (b) vas deferens (c) oviduct (d) urethra
Answer: (b)
16. In the list of organisms given below, those
that reproduce by the asexual method are
(i) banana (ii) dog (iii) yeast (iv) Amoeba 1 👇
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(i) banana (ii) dog (iii) yeast (iv) Amoeba 1 👇
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer: (b)
17. In the following questions, the Assertion and
The reason has been put forward. Read the statements carefully and choose the
correct alternative from the following: 1 👇
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion:
Amoeba reproduced by fission
Reason: All unicellular organisms reproduced by the asexual method.
Reason: All unicellular organisms reproduced by the asexual method.
Answer: (a) Both the Assertion and the Reason are correct and the Reason
is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
18. In the
following questions, the Assertion and Reason have been put forward. Read the
statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following: 1 👇
explanation
of the Assertion.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
(b) The Assertion and the Reason are correct but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Assertion:
In human beings, the female play a major role in determining the sex of the
offspring.
Reason: Women have two X chromosomes.
Reason: Women have two X chromosomes.
Answer: (d) The statement of the Assertion is false but the Reason is
true.
19. The gestation period in human beings is about
__________ days. 1 👇
Answer: 280.
20. The process of release of an egg from the
ovary is called __________. 1 👇
Answer: ovulation.
21. The development of the foetus inside the uterus
till birth is called __________.
1 👇
Answer: gestation.
22. The attachment of the embryo to the uterus is
called __________. 1 👇
Answer: implantation.
23. Sterilisation in males is called ______. 1 👇
Answer: a vasectomy.
24. The ability of a cell to divide into several
cells during reproduction in ___________ is called ______________. 1 👇
Answer: Plasmodium, multiple fission.
25. The disease ___________ is caused by
microorganism known as _________. 1 👇
Answer: kala-azar, leishmania.
How do Organisms Reproduce?
26. The organism like ___________ can reproduce
by the method of___________.
1 👇
Answer: spirogyra, fragmentation
27. In Rhizopus the fine thread-like structures
spread on the whole surface of a slice of bread are called _______________. 1 👇
Answer: hyphae.
28. A tiny animal having tentacles which
reproduce by growing buds on the side of its body is _______________.
1 👇
Answer: hydra.
29. The importance of variations in organisms is
that it helps the species of various organisms to survive in an adverse
environment [True/False] 1 👇
Answer: True.
30. Complex multicellular organisms cannot give
rise to new organisms through budding. [True/False] 1 👇
Answer: True.
31. Testes are the primary reproductive organs in
man. [True/False] 1 👇
Answer: True.
32. An embryo is formed by the growth and
development of a foetus. [True/False]
1👇
Answer: False.
33. An important feature of the barrier method is
that it protects a person from STDs. [True/False] 1 👇
Answer: True.
34. The killing of the unborn girl child is
called female foeticide. [True/False] 1 👇
Answer: True.
35. The surgical procedure carried out in females
is called vasectomy. [True/False]
1 👇
Answer: False.
36. Copper-T cannot protect from acquiring
sexually transmitted diseases [True/False] 1👇
Answer: True.
37. Gonorrhoea and syphilis are caused by
bacteria. [True/False] 1 👇
Answer: True.
38. Match column I with Column II. 1 👇
Column I
|
Column II
|
(i) Placenta
(ii) Male gametes of a plant (iii) Budding (iv) Amoeba (v) Vegetative propagation by leaves |
(A) Binary fission
(B) Bryophyllum (C) Nourishment of embryo (D) Yeast (E) Pollen grains |
Answer: (i) (C), (ii) (E), (iii) (D), (iv) (A), (v) (B)
39. Match column I with Column II. 1 👇
Column I
|
Column II
|
(i) Fission
(ii) Fragmentation (iii) Regeneration (iv) Budding |
(A) Spirogyra
(B) Hydra (C) Bryophyllum (D) Amoeba (E) Planaria |
Answer: (i) (C), (ii) (A), (iii) (D), (iv) (B)
40. What is vegetative propagation? 1 👇
Answer: It is the method of obtaining new plants from the parts of
parent plants like stems, roots and leaves, without the help of any reproductive
organ.
41. Name the part of Bryophyllum where
the buds are produced for vegetative propagation. 1 👇
Answer: Vegetative
part, the leaf is used in the propagation of Bryophyllum.
42. Select two plants raised by the method of
vegetative propagation from the list given below: 1 👇
banana, gram, rose, tomato, wheat, jasmine.
banana, gram, rose, tomato, wheat, jasmine.
Answer: Banana, jasmine and rose are raised by the vegetative method.
43. Name the method by which Hydra reproduces.
Is this method sexual or asexual? 1 👇
Answer: Hydra reproduces by budding. It is an asexual
method.
44. What are those organisms called which bear
both the sex organs in the same individual? Give one example of such an organism. 1 👇
Answer: Organisms which bear both the sex organs are called
hermaphrodite/bisexual.
Example: Earthworm.
Example: Earthworm.
45. List two functions of the ovary of the human female
reproductive system. 1 👇
Answer: Functions of the ovary are:
(i) production of the female gamete, ovum.
(ii) secretion of female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.
(i) production of the female gamete, ovum.
(ii) secretion of female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.
46. Name the life process of an organism that
helps in the growth of its population. 1 👇
Answer: Reproduction.
47. Name two simple organisms having the ability
of regeneration. 1 👇
Answer: Hydra and Planaria.
48. Malarial parasite divides into many daughter
individuals simultaneously through multiple fission. State an advantage the
parasite gets because of this type of reproduction. 1 👇
Answer: Due to multiple fission progeny of malarial parasite is identical
like a parent and single individual can reproduce in large number.
49. State what type of method is used for growing
jasmine plant. 1 👇
Answer: Artificial methods of vegetative propagation like layering is
used for growing jasmine plant.
50. Name the type of fission carried out by Amoeba. 1 👇
Answer: The type of fission carried out by Amoeba is binary fission.
How do Organisms Reproduce?
51. Where is DNA found in a cell? 1 👇
Answer: DNA is found in the nucleus.
52. What is DNA? 1 👇
Answer: The full form of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA lies in the
cell nucleus which is the information source for making proteins and different proteins lead to different designs.
53. Why is DNA copying necessary during
reproduction? 1 👇
Answer: During reproduction, an organism gives birth to another organism whose body design is similar to the parents. DNA contains the body design information and hence, during reproduction the DNA is copied to give birth to
an organism of similar body design.
54. Name the information source of making
proteins in the cell. State two basic events in reproduction. 1 👇
Answer: The DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source of making proteins.
The two basic events in reproduction are:
(i) creation of a DNA copy
(ii) the function of additional cellular apparatus by the cell, involved in the
process.
55. What is the effect of DNA copying which is
not perfectly accurate on the reproduction process? 1 👇
Answer: DNA copying is not perfectly accurate and the resultant errors
are a source of variations in populations of organisms.
56. What is a bisexual flower? Give one example. 1 👇
Answer: A bisexual flower is a flower that contains both stamens and
carpel. Example: Hibiscus.
57. Name the parts of a bisexual flower that are
not directly involved in reproduction. 1 👇
Answer: Parts of a bisexual flower which are not directly involved in reproduction are (i) Petal, (ii) Sepal and (iii) Stem.
58. Write suitable conditions necessary for seed
germination. 1 👇
Answer: Conditions necessary for seed germination are water, temperature
and oxygen.
59. Mention the mode of reproduction used by 1 👇
(a) Amoeba (b) Planaria
(a) Amoeba (b) Planaria
Answer: Mode of reproduction used by
(a) Amoeba is binary fission.
(b) Planaria is regeneration.
(a) Amoeba is binary fission.
(b) Planaria is regeneration.
60. Name the floral parts of a plant that develop
into (i) Fruit (ii) Seeds 1 👇
Answer: (i) Fruit: Ovary (ii) Seed: Ovule
61. Name the part of the female reproductive system
where the egg is fertilized.
1 👇
1 👇
Answer: Egg gets fertilized in the oviduct.
62. What is the average duration of human
pregnancy? 1 👇
Answer: The average duration of human pregnancy is 40 weeks or 280 days.
63. Why is sexual reproduction considered to be
superior to asexual reproduction in terms of evolution? 1 👇
Answer: Sexual mode of reproduction is a source of variation (in a
population of organisms) which ensures the survival of the species.
64. Name the largest cell present in the human
body. 1 👇
Answer: The largest cell present in the human body is the ovum.
65. Name the hormones responsible for secondary
sexual characters in
(i) Girls (ii) Boys. 1 👇
(i) Girls (ii) Boys. 1 👇
Answer:
(i) Girls: Estrogen and progesterone
(ii) Boys: Testosterone
(ii) Boys: Testosterone
66. What is Gestation period? 1 👇
Answer: The period from the development of the foetus until birth is
called the gestation period.
67. Name the causative agent of the disease
“Kala-azar” and its mode of asexual reproduction. 1 👇
Answer: Leishmania causes kala-azar. It reproduces by binary
fission.
68. How does the chemical method help in
preventing pregnancy? 1 👇
Answer: The chemical method prevents ovaries from releasing egg and
hence fertilization cannot take place.
69. Define reproduction. How does it help in
providing stability to the population of species? 3 👇
Answer: Reproduction: It is the process of producing new individuals of
the same species by existing organisms of a species, i.e. parents.
Reproduction helps in providing stability to the population of species because
reproduction is a process by which organisms increase their populations. The
rate of birth and death in a given population determine its size.
71. What happens when 3 👇
(a) Planaria gets cut into two pieces?
(b) A mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length?
(c) On maturation sporangia burst?
(a) Planaria gets cut into two pieces?
(b) A mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length?
(c) On maturation sporangia burst?
Answer: (a) When Planaria gets cut into two pieces, each piece grows
into a complete organism.
(b) A mature Spirogyra on attaining considerable length breaks up into two or
more small pieces. Each piece then grows into a new individual.
(c) When sporangia bursts, spores are released, each one of which develops into a new individual.
(c) When sporangia bursts, spores are released, each one of which develops into a new individual.
72. Explain budding in Hydra with the help of
labelled diagrams only. 3 👇
73.
(a) Name the following: 3👇
(i) A thread like non-reproductive structures present
in Rhizopus.
(ii) ‘Blobs’ that develop at the tips of the non-reproductive threads in Rhizopus.
(b) Explain how these structures protect themselves and what is the function of the structures released from the ‘blobs’ in Rhizopus.
(ii) ‘Blobs’ that develop at the tips of the non-reproductive threads in Rhizopus.
(b) Explain how these structures protect themselves and what is the function of the structures released from the ‘blobs’ in Rhizopus.
Answer:
(a) (i) Hyphae (ii) Sporangium
(b) Spores are enclosed within sporangia which protects the spores.
Spores, when released from sporangia, develop into new Rhizopus.
(b) Spores are enclosed within sporangia which protects the spores.
Spores, when released from sporangia, develop into new Rhizopus.
74. List three distinguishing features between
sexual and asexual types of
reproduction, in tabular form. 3 👇
Answer: Distinguishing features between sexual and asexual reproduction:
75. Explain the process of regeneration in
Planaria. How is this process different from reproduction? 3 👇
Answer: If a Planaria is cut into any number of pieces,
each piece will grow into a complete organism. Regeneration is carried out by
specialised cells which proliferate and make a large number of cells and then
tissues.
In regeneration, the organism needs to be cut into pieces to get more
organisms. In reproduction, the organism need not be cut to multiply.
How do Organisms Reproduce?
76. Explain vegetative propagation with the help of two examples. List two advantages of vegetative propagation. 3 👇
76. Explain vegetative propagation with the help of two examples. List two advantages of vegetative propagation. 3 👇
Answer: Vegetative propagation: In vegetative propagation, new plants
are obtained from the parts of old plants, like stems, roots and leaves,
without the help of any reproductive organ.
There are two ways of vegetative propagation :(a) Natural vegetative propagation
(b) Artificial vegetative propagation
Natural vegetative propagation by leaves: The fleshy leaves of Bryophyllum bear
adventitious buds in the notches along the leaf margin.
Artificial vegetative propagation like grafting: In this method of
reproduction, two plants of closely related varieties are joined together so
that they live as one plant.
Two advantages of vegetative propagation:(i) Vegetative propagation is a cheaper, easier and more rapid method of propagation in plants than growing plants from their seeds.
(ii) Better quality of the plants can be maintained by this method.
77. Illustrate the following with the help of
suitable diagrams : 3 👇
(i) Spore formation in Rhizopus
(ii) Multiple fission in Plasmodium
(i) Spore formation in Rhizopus
(ii) Multiple fission in Plasmodium
Answer:
(i) Spore formation in Rhizopus.
(ii) Multiple fission in Plasmodium
78.
1.
Identify the organisms in figure A, B, C and D. 3 👇
2. Identify the life process shown in all the figures.
3. How is this life process advantageous to the organisms?
Answer:
1. A. Hydra B. Rhizopus C. Bryophyllum D. Planaria
2. The life process shown in the figures is the asexual mode of reproduction.
3. This life process is advantageous to the organisms because
(i) Only one individual is required.
(ii) Large numbers of offsprings are produced.
2. The life process shown in the figures is the asexual mode of reproduction.
3. This life process is advantageous to the organisms because
(i) Only one individual is required.
(ii) Large numbers of offsprings are produced.
79. (i) Which are the two main types of
reproduction in living organisms? 3 👇
(ii) Classify the following under these two types:
Amoeba, Frog, Earthworm, Yeast
(ii) Classify the following under these two types:
Amoeba, Frog, Earthworm, Yeast
Answer:
(i) The two main types of reproduction in living organisms are – Asexual
reproduction and sexual reproduction.
(ii) Asexual reproduction: Amoeba, yeast
Sexual reproduction: Frog, earthworm
(ii) Asexual reproduction: Amoeba, yeast
Sexual reproduction: Frog, earthworm
80. What is DNA copying? State its importance. 3 👇
Answer: DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source for making
proteins and different proteins lead to different body designs. During
reproduction, a similar copy of DNA is generated and the process is called DNA
copying. Importance of DNA copying are:
(i) DNA copying provides cellular apparatus in the daughter cells.(ii) DNA in daughter cells will be able to control the functioning of the daughter cells.
(iii) DNA copies will retain the trait.
81. What are chromosomes? Explain how in sexually
reproducing organisms the number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained. 3 👇
Answer: ‘Chromosomes’ are long thread-like structures which contain
hereditary information of the individual and are thereby the carriers of genes.
Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of a cell.
The parents are diploid (2n) as each of them has two sets of chromosomes. They
form haploid (1n) male and female gametes through the process of meiosis. The
haploid gametes have one set of chromosomes. These two gametes fuse during
fertilisation and the offspring become diploid (2n) which is same as parents
chromosome number.
82. Write the full form of DNA. Name the part of
the cell where it is located. Explain its role in the process of reproduction
of the cell. 3👇
Answer: The full form of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the genetic
the material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus of a cell.
Role of DNA in the process of reproduction of the cell:
DNA plays an important role in the reproduction of a cell. The reproducing cell
produces an identical copy of DNA through some cellular mechanism. Since the
newly formed copy of DNA lacks an organised cellular structure, the cell gets
divided to provide cell cover to the newly formed DNA. Thus, two daughter cells
are formed from a single cell as a result of the copying of DNA.
83. Name the parts A, B and C shown in the
following diagram and state one function of each. 3 👇
Answer:
A = Anther of the stamen.
Function- Anther contains two pollen sacs within which numerous pollen grains are produced.
B = Carpel
Function—It is the female reproductive organ of a flower which receives pollen grains that move through the style and causes fertilisation in the ovaries.
C = Ovule
Function: Ovule contains female gamete, egg.
Function- Anther contains two pollen sacs within which numerous pollen grains are produced.
B = Carpel
Function—It is the female reproductive organ of a flower which receives pollen grains that move through the style and causes fertilisation in the ovaries.
C = Ovule
Function: Ovule contains female gamete, egg.
84. What is meant by pollination? Name and
differentiate between the two modes of pollination in flowering plants. 3 👇
Answer: Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of
a stamen to the stigma of a carpel. The two modes of pollination are self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Self-pollination
|
Cross-pollination
|
(i) Self-pollination occurs within a flower or between two flowers of the same plant.
|
(i) Cross-pollination occurs between two flowers borne on different plants of the same species.
|
(ii) Flowers do not depend on other agencies for pollination.
|
(ii) Agents such as insects, water and wind are required for pollination.
|
(iii) Pollen grains are produced in small numbers.
|
(iii) Pollen grains are produced in large numbers.
|
85. Identify A, B and C in the given diagram and write one function of each. 3 👇
A = Stigma
B = Pollen tube
C = Female germ cell
The function of stigma: Stigma helps in receiving the pollen grains from the anther of stamen during pollination.
The function of the pollen tube: The pollen tube facilitates the movement of male germ cell through it to reach the female germ cell.
The function of female germ cell: It meets with the male germ cell to form a zygote which divides many times to form an embryo.
B = Pollen tube
C = Female germ cell
The function of stigma: Stigma helps in receiving the pollen grains from the anther of stamen during pollination.
The function of the pollen tube: The pollen tube facilitates the movement of male germ cell through it to reach the female germ cell.
The function of female germ cell: It meets with the male germ cell to form a zygote which divides many times to form an embryo.
86. Name the two reproductive parts of a bisexual
flower which contain the germ cells. State the location and function of its
female reproductive part. 3 👇
Answer: The two reproductive parts of a bisexual flower are stamen and
carpel. The carpel is the female reproductive organ located at the centre of a
flower. It consists of an ovary, style and stigma. The ovary is the swollen part
at the bottom of the carpel. The elongated part in the centre of the carpel is
the style. The stigma is sticky so that it can trap pollen grains easily.
Pollen tube that grows from the pollen grain to the ovary aids fertilisation.
87. List any three differences between
pollination and fertilisation. 3 👇
Answer: Differences between:
Pollination
|
Fertilisation
|
(i) It is the transfer of pollen
grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower.
|
(i) It is the fusion of male and
female gametes.
|
(ii) Pollination precedes
fertilisation.
|
(ii) Fertilisation occurs only after pollination when the pollen grain has germinated and sent the male gametes to the ovule.
|
(iii) Pollination carries the male gamete producing pollen grains to the female sex organ.
|
(iii) Fertilisation brings about the fusion of gametes.
|
88. What is vegetative propagation? When is it
used? Name three methods of vegetative propagation. 3 👇
Answer: The method of developing new plants from the vegetative parts of
a plant, such as a root, stem or leaf is called vegetative propagation.
Vegetative propagation can be classified into natural and artificial methods.
The method of vegetative propagation is used when some plants like banana,
orange rose and jasmine has lost the capacity to produce seeds.
The three methods of vegetative propagation are cutting, layering and grafting.
89. Differentiate between ‘self-pollination’ and
‘cross-pollination’. Describe ‘double fertilisation’ in plants. 3 👇
Answer:
Differences
between:
Self-pollination
|
Cross-pollination
|
(i) Self-pollination occurs within
a flower or between
two flowers of the same plant. |
(i) Cross-pollination occurs between two flowers borne on different plants of the same species.
|
(ii) Flowers do not depend on other agencies for pollination.
|
(ii) Agents such as insects, water and wind are required for pollination.
|
(iii) Pollen grains are produced in small numbers.
|
(iii) Pollen grains are produced in large numbers.
|
During fertilisation in plants, the following events take place :
(i) One of the male gametes fuses with the female gamete present in the embryo sac.
(ii) The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei in the embryo sac.
The first fusion product gives rise to the zygote while the second one forms the endosperm. The process of fusion occurring twice in the embryo sac is called double fertilisation.
90. Suggest three contraceptive methods to
control the size of the human population which is essential for the health and
the prosperity of a country. State the basic principle moved in each. 3 👇
Answer: Three contraceptive methods that can be used to control the size of
human population are:
(i) Mechanical barrier method: In this method, physical devices such as condoms
are used. The principle used is that it prevents entry of sperm into the female
genital tract during copulation and thus acting as a barrier between them.
(ii) Chemical method: In this method, specific drugs are used by females which
are of two types-oral pills and vaginal pills. The principle used is that it
contains hormones which stop the ovaries from releasing ovum into the fallopian
tube.
(iii) Surgical method: In this method, a small portion of vas deferens in male
and the fallopian tube in the female is surgically removed or tied. The principle used
is that meeting of sperm and egg in the fallopian tube is prevented.
91. What is sexual reproduction? List its four significances. 3 👇
Answer: Sexual reproduction: It is the process of producing a new organism
from two parents by making use of their sex cells or gametes.
(i) Sexual reproduction needs two individuals, one male and one female.
(ii) Variations are more in sexual reproduction.
(iii) Sexual reproduction gives a survival advantage to a species.
(iv) Sex cells of organisms engaged in sexual reproduction have chromosome
number half of the other cells of the organism.
92. List six specific characteristics of sexual
reproduction. 3👇
Answer: Specific characteristics of sexual mode of reproduction.
(i) Sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters in the offsprings.
(ii) It results in new combinations of genes brought together in the gamete and this reshuffling increases genetic variation.
(iii) It plays a prominent role in the origin of new species.
(iv) The sexual mode of reproduction incorporates the process of combining DNA from two different individuals during reproduction.
(v) It needs two parents to produce offspring.
(vi) Sex cells are used in sexual reproduction.
(i) Sexual reproduction promotes diversity of characters in the offsprings.
(ii) It results in new combinations of genes brought together in the gamete and this reshuffling increases genetic variation.
(iii) It plays a prominent role in the origin of new species.
(iv) The sexual mode of reproduction incorporates the process of combining DNA from two different individuals during reproduction.
(v) It needs two parents to produce offspring.
(vi) Sex cells are used in sexual reproduction.
Answer: Four methods of contraception used by humans are:
(i) A mechanical barrier such as a condom.
(ii) A surgical method such as vasectomy or tubectomy.
(iii) A chemical method such as the oral or vaginal pill.
(iv) Copper-T.
Advantages of using contraceptives.
(a) It helps in avoiding unwanted pregnancy.
(b) Condom helps in preventing the transmission of STDs.
(i) A mechanical barrier such as a condom.
(ii) A surgical method such as vasectomy or tubectomy.
(iii) A chemical method such as the oral or vaginal pill.
(iv) Copper-T.
Advantages of using contraceptives.
(a) It helps in avoiding unwanted pregnancy.
(b) Condom helps in preventing the transmission of STDs.
94.
(a) Name the human male reproductive organ that produces sperms and also secretes a hormone. Write the functions of the secreted hormone.
(b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where
(i) fertilisation takes place,
(ii) implantation of the fertilised egg occurs. 3 👇
(a) Name the human male reproductive organ that produces sperms and also secretes a hormone. Write the functions of the secreted hormone.
(b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where
(i) fertilisation takes place,
(ii) implantation of the fertilised egg occurs. 3 👇
Answer:
(a) Sperms are produced by testes in the male reproductive system. Testes
also secrete male sex hormone, called testosterone. Testosterone brings about
changes in appearance in boys at the time of puberty.
(b) (i) Fertilisation occurs in the fallopian tube.
(ii) Implantation of the fertilized egg takes place in the uterus.
(b) (i) Fertilisation occurs in the fallopian tube.
(ii) Implantation of the fertilized egg takes place in the uterus.
95. What is the placenta? Explain its function in
humans. 3 👇
Answer: Placenta in human female is a complex double-layered spongy
vascular tissue formed by the joint activity of maternal and foetal tissues in
the wall of the uterus. It is meant for attachment, nourishment and waste disposal
for the foetus.
Through the placenta, the foetus gets nutrients and oxygen from the mother. Waste
products from the foetus are also transported to the mother through the placenta.
96. List two functions of each one of the
following parts of the human female reproductive system: 3 👇
(i) Ovaries (ii) Fallopian tubes (iii) Uterus
(i) Ovaries (ii) Fallopian tubes (iii) Uterus
Answer:
(i) Ovaries:
(a) They produce female gametes.
(b) They secrete female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.
(ii) Fallopian tubes:
(a) They carry eggs from ovaries to the uterus.
(b) They allow sperm to travel to meet the egg.
(iii) Uterus:
(a) It allows implantation of zygote on its wall.
(b) It causes menstruation when the egg is not fertilized.
(a) They produce female gametes.
(b) They secrete female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.
(ii) Fallopian tubes:
(a) They carry eggs from ovaries to the uterus.
(b) They allow sperm to travel to meet the egg.
(iii) Uterus:
(a) It allows implantation of zygote on its wall.
(b) It causes menstruation when the egg is not fertilized.
97. (i) Give two reasons for avoiding frequent
pregnancies by women. 3 👇
(ii) Explain the following methods of contraception giving one example of each.
(a) Barrier method. (b) Surgical method.
(ii) Explain the following methods of contraception giving one example of each.
(a) Barrier method. (b) Surgical method.
Answer:
(i) Pregnancy makes major demand on the body and the mind of a woman. If
she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected. Frequent
pregnancies should, therefore, be avoided so that the health of the woman is not
adversely affected.
(ii) (a) Barrier Method: In these methods, physical devices such as condoms, diaphragm
and cervical caps are used. These devices prevent the entry of sperm in the
female genital tract during copulation, thus acting as a barrier between them.
(b) Surgical Method: In this method, a small portion of vas deferens in male
and the fallopian tube in the female is surgically removed or tied. It is called
vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females. In this case, if the vas deferens
in male is blocked, sperm transfer will be prevented and if the fallopian tube
in the female is blocked, the egg will not be able to reach the uterus, thus
fertilisation will not take place.
98. (i) What is fertilisation? Distinguish
between external fertilisation and internal fertilisation.
(ii) Which is the site of fertilisation in human beings? 3 👇
(ii) Which is the site of fertilisation in human beings? 3 👇
Answer:
(i) Fertilisation is defined as the fusion of a male gamete (sperm) with
a female gamete (an ovum or egg) to form a zygote during sexual reproduction.
Differences between:
External Fertilisation
|
Internal Fertilisation
|
(i) The fusion of male gamete
(sperm) and female gamete (ovum) occurs outside the body.
|
(i) The fusion of gametes occurs inside the body.
|
(ii) Both individuals discharge their gametes outside the body.
|
(ii) Only the male discharges sperms into the female genital tract.
|
(iii) Development occurs outside the body.
|
(iii) Development occurs inside the
body.
|
(iv) Example: Frog.
|
(iv) Examples: Human, birds,
cattle, etc.
|
99. What are the male and female gonads in human
beings? State any two functions of each of them. 3👇
Answer: Male gonads are Testis and female gonads are ovaries in human beings.
Functions of Testis:
(i) Testis produces sperms, the male haploid gametes.
(ii) They produce male sex hormone, i.e. testosterone.
Functions of Ovaries:
(i) They produce ova, the female haploid gametes.
(ii) They produce female sex hormones, i.e. estrogen and progesterone.
Functions of Testis:
(i) Testis produces sperms, the male haploid gametes.
(ii) They produce male sex hormone, i.e. testosterone.
Functions of Ovaries:
(i) They produce ova, the female haploid gametes.
(ii) They produce female sex hormones, i.e. estrogen and progesterone.
100. Draw a well-labelled diagram of the human female
reproductive system. Explain the menstrual cycle of the female. 3 👇
Answer:
The uterus prepared itself every month to receive and nurture the
fertilized egg. The lining of the uterus thickens and is richly supplied with
blood to nourish the embryo. If the egg is not fertilized, the thick and
nourishing lining of the uterus breaks and comes out through vagina as blood
and mucus which is called menstruation. The cycle of events taking place in the
ovaries and uterus every twenty-eight days and marked by menstrual flow is
called the menstrual cycle.
How do Organisms Reproduce?
How do Organisms Reproduce?
101. In human females, what happens when
(i) the egg is fertilised
(i) the egg is fertilised
(ii) the egg is not fertilised? 3 👇
Answer: The lining of the uterus becomes
thick and spongy before release of an egg.
(i) If the egg is fertilized, it moves up to the uterus and gets implanted on the uterus. The uterine wall thickens and richly supplied with blood. The region between the embryo and uterine wall grows into placenta which provides nourishment and oxygen to the embryo. The child is borne as a result of the rhythmic contraction of the uterine muscle.
(ii) If the egg is not fertilized, the thick and nourishing lining of the uterus breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus which is called menstruation.
(i) If the egg is fertilized, it moves up to the uterus and gets implanted on the uterus. The uterine wall thickens and richly supplied with blood. The region between the embryo and uterine wall grows into placenta which provides nourishment and oxygen to the embryo. The child is borne as a result of the rhythmic contraction of the uterine muscle.
(ii) If the egg is not fertilized, the thick and nourishing lining of the uterus breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus which is called menstruation.
102. (a) In the human body, what is the role of
(i) seminal vesicles and (ii) prostate gland?
(b) List two functions performed by the testis in human beings. 3 👇
(i) seminal vesicles and (ii) prostate gland?
(b) List two functions performed by the testis in human beings. 3 👇
Answer:
(a) The role of seminal vesicles and the prostate gland are as follows:
(i) Seminal vesicles produce seminal plasma which in the form of fluid makes the transport of sperms smooth and also provide nourishment to them.
(ii) The prostate gland secretes prostatic fluid that keeps the sperms alive and helps them to swim vigorously.
(b) Two functions performed by the testis in human beings are as follows:
(i) Formation of sperms takes place in testis.
(ii) Testis secrete the hormone testosterone which regulates the formation of sperms and brings changes in the appearance of boys at the time of puberty.
(i) Seminal vesicles produce seminal plasma which in the form of fluid makes the transport of sperms smooth and also provide nourishment to them.
(ii) The prostate gland secretes prostatic fluid that keeps the sperms alive and helps them to swim vigorously.
(b) Two functions performed by the testis in human beings are as follows:
(i) Formation of sperms takes place in testis.
(ii) Testis secrete the hormone testosterone which regulates the formation of sperms and brings changes in the appearance of boys at the time of puberty.
103. List any four methods of contraception used
by humans. How does their use have a direct effect on the health and prosperity
of a family? 3 👇
Answer: Four methods of contraception used by humans are:
(i) A mechanical barrier such as a condom.
(ii) A surgical method such as vasectomy for male and tubectomy for female.
(iii) A chemical method such as oral and vaginal pills.
(iv) Copper-T
Sexual act always has the potential for pregnancy. Pregnancy makes major demand on the body and mind of the woman, and if she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected. Contraceptive methods help in avoiding pregnancy and also help in keeping the gap between two children so that the woman’s body recovers. These methods help in a limited number of children to one or two. If the family size is small, the family can save some amount after meeting the day to day expenditure. This will improve the economic condition of the family and the family will prosper.
(i) Gonorrhoea and Syphilis are STDs caused by a bacterial infection.
(ii) AIDS and genital Warts are STDs caused by a viral infection.
The spread of STDs can be prevented by:
(a) Avoiding sexual contact with infected persons.
(b) Using a condom for the penis during sexual activity.
105. List four points of significance of reproductive health in a society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years in our country. 3 👇
(i) A mechanical barrier such as a condom.
(ii) A surgical method such as vasectomy for male and tubectomy for female.
(iii) A chemical method such as oral and vaginal pills.
(iv) Copper-T
Sexual act always has the potential for pregnancy. Pregnancy makes major demand on the body and mind of the woman, and if she is not ready for it, her health will be adversely affected. Contraceptive methods help in avoiding pregnancy and also help in keeping the gap between two children so that the woman’s body recovers. These methods help in a limited number of children to one or two. If the family size is small, the family can save some amount after meeting the day to day expenditure. This will improve the economic condition of the family and the family will prosper.
104. What are sexually transmitted diseases? List
two example of each disease caused due to (i) bacterial infection and (ii)
viral infection. Which device or devices may be used to prevent the spread of
such diseases. 3 👇
Answer: STDs are diseases
which spread by sexual contact from an infected person to a healthy person.(i) Gonorrhoea and Syphilis are STDs caused by a bacterial infection.
(ii) AIDS and genital Warts are STDs caused by a viral infection.
The spread of STDs can be prevented by:
(a) Avoiding sexual contact with infected persons.
(b) Using a condom for the penis during sexual activity.
105. List four points of significance of reproductive health in a society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years in our country. 3 👇
Answer:
(i) The mother carrying a child should be physically matured.
(ii) The mother should be mentally fit to take care of the child.
(iii) There should be at least 3 years gap between 2 children.
(iv) Nutritious food should be available to the mother during pregnancy and during the lactation period.
(ii) The mother should be mentally fit to take care of the child.
(iii) There should be at least 3 years gap between 2 children.
(iv) Nutritious food should be available to the mother during pregnancy and during the lactation period.
106. List
and explain in brief three methods of contraception. 3 👇
Answer:
Methods of contraception are:
(i) Use of condom for penis or for the vagina as a mechanical barrier for the sperms to reach the egg.
(ii) Use of oral pills which change the hormonal balance in female, so that eggs are not released.
(i) Use of condom for penis or for the vagina as a mechanical barrier for the sperms to reach the egg.
(ii) Use of oral pills which change the hormonal balance in female, so that eggs are not released.
(iii) Surgical method where either the vas deferens of the male is blocked or the
fallopian tube of the female is blocked.
107. What is AIDS? Which microbe is responsible
for AIDS infection? State one mode of transmission of this disease. Explain in
brief one measure for the prevention of AIDS.
3 👇
Answer:
AIDS is the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
It is caused by a virus called Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
AIDS is transmitted by sexual contact with an infected person.
AIDS can be prevented by avoiding sexual contact with an infected person or by using a condom during sex.
It is caused by a virus called Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
AIDS is transmitted by sexual contact with an infected person.
AIDS can be prevented by avoiding sexual contact with an infected person or by using a condom during sex.
108. What does HIV stand for? Is AIDS an
infectious disease? List any four modes of spreading AIDS.
Answer:
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
Yes, AIDS is an infectious disease.
Four modes of spreading AIDS are as follows:
(i) By having sexual contact with an infected person.
(ii) By the transfusion of blood from an infected person.
(iii) Through infected needles used for injection.
(iv) Through the placenta from the mother to child during pregnancy.
Yes, AIDS is an infectious disease.
Four modes of spreading AIDS are as follows:
(i) By having sexual contact with an infected person.
(ii) By the transfusion of blood from an infected person.
(iii) Through infected needles used for injection.
(iv) Through the placenta from the mother to child during pregnancy.
109. Expand AIDS. List any four methods of
prevention (control) of AIDS.
Answer: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Four methods of prevention or control of AIDS are as follows :
(i) Using a condom during sex.
(ii) Avoiding sharing of needles or the use of disposable needles.
(iii) Testing blood for AIDS before transfusion.
(iv) Avoiding sexual contact with an unknown person.
Four methods of prevention or control of AIDS are as follows :
(i) Using a condom during sex.
(ii) Avoiding sharing of needles or the use of disposable needles.
(iii) Testing blood for AIDS before transfusion.
(iv) Avoiding sexual contact with an unknown person.
110. (a) List any four reasons for adopting
contraceptive methods.
(b) If a woman is using Copper-T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases? Why?
(b) If a woman is using Copper-T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases? Why?
Answer:
(a) Four reasons for adopting contraceptive methods are:
(i) To increase the gap between two children.
(ii) To prevent unwanted pregnancy.
(iii) To prevent transmission of STD.
(iv) To control population growth.
(b) If a woman is using a copper-T, it will not help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases. Copper-T prevents the only implantation in the uterus.
(i) To increase the gap between two children.
(ii) To prevent unwanted pregnancy.
(iii) To prevent transmission of STD.
(iv) To control population growth.
(b) If a woman is using a copper-T, it will not help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases. Copper-T prevents the only implantation in the uterus.
111. Explain the following methods of
contraception giving one example of each:
(i) Barrier method
(ii) Hormonal imbalance method
(iii) Surgical method
(i) Barrier method
(ii) Hormonal imbalance method
(iii) Surgical method
Answer:
(i) Barrier Method. In these methods, physical devices such as condoms,
diaphragm and cervical caps are used. These devices prevent the entry of sperm
in the female genital tract during copulation, thus acting as a barrier between
them.
(ii) Hormonal Imbalance Method. In this method, specific drugs are used by females, which are of two types — oral pills and vaginal pills.
Oral Pills contain hormones which stop the ovaries from releasing ovum into the fallopian tube. These pills are also called oral contraceptives (OCs) which acts by changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released and fertilisation cannot occur.
(iii) Surgical Method. In this method, a small portion of vas deferens in male and the fallopian tube in the female is surgically removed or tied. It is called vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females. In this case, if the vas deferens in male is blocked, sperm transfer will be prevented and if the fallopian tube in the female is blocked, the egg will not be able to reach the uterus, thus fertilisation will not take place.
(ii) Hormonal Imbalance Method. In this method, specific drugs are used by females, which are of two types — oral pills and vaginal pills.
Oral Pills contain hormones which stop the ovaries from releasing ovum into the fallopian tube. These pills are also called oral contraceptives (OCs) which acts by changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released and fertilisation cannot occur.
(iii) Surgical Method. In this method, a small portion of vas deferens in male and the fallopian tube in the female is surgically removed or tied. It is called vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females. In this case, if the vas deferens in male is blocked, sperm transfer will be prevented and if the fallopian tube in the female is blocked, the egg will not be able to reach the uterus, thus fertilisation will not take place.
112. What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name
four such diseases. Which one damages the immune system of the human body?
Answer: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) are the diseases which
spread by sexual contact from an infected person to a healthy person. They are
caused by various microorganisms that live in warm and moist environments of
the vagina, urethra, anus and mouth.
The four sexually transmitted diseases are
(i) Gonorrhoea (ii) Syphilis
(iii) Trichomoniasis (iv) AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome).
AIDS damages the immune system of the human body.
The four sexually transmitted diseases are
(i) Gonorrhoea (ii) Syphilis
(iii) Trichomoniasis (iv) AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome).
AIDS damages the immune system of the human body.
113. List in tabular form the two differences
between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Name and explain with the help
of a labelled diagram the process by which Hydra reproduces asexually. 5 👇
Answer:
Sexual Reproduction
|
Asexual Reproduction
|
(i) In sexual reproduction, two
parents take part.
(ii) Variation occurs in the offsprings. |
(i) In asexual reproduction, a
single parent is involved.
(ii) Offsprings are genetically identical to each other and to their parents.
|
Reproduction in Hydra:
- Hydra
reproduces by budding using the regenerative cells.
- A
bud develops as an outgrowth in Hydra due to repeated cell division at one specific site.
- When
fully mature, the bud detaches itself from the parent body and develops into a new independent individual.
114. (a) What is fragmentation in organisms?
Name a multicellular organism which reproduces by this method.
(b) What is regeneration in an organism? Describe regeneration in Planaria with the help of a suitable diagram.
(b) What is regeneration in an organism? Describe regeneration in Planaria with the help of a suitable diagram.
Answer:
(a) Fragmentation. Multicellular organisms with simple body organisation
such as filamentous algae-Spirogyra break up into two or more small pieces or
fragments upon maturation. These fragments grow into new individuals.
(b) Regeneration is the ability of a fully differentiated organism to
give rise to new individual organisms from ITS body parts.
- Small
cut or broken parts of the organism body, grow or regenerate into separate
individuals.
- Planaria
can be cut into any number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete
organism.
- Regeneration
is carried out by specialised cells which proliferate and make large number of cells.
- The
changes take place in an organised sequence for development.
115. List any four modes of asexual reproduction.
Give one example of each. Explain any two modes of asexual reproduction.
Answer: Four modes of asexual reproduction are:
(i) Fission, e.g. Amoeba (ii) Fragmentation, e.g. Spirogyra
(iii) Regeneration, e.g. Planaria (iv) Budding, e.g. Hydra
Binary fission: It is the division of one cell into two similar cells. In this method, the nucleus first divides amitotically into two, followed by the division of the cytoplasm. The cell finally splits into two daughter cells.
Budding: In budding, a small part of the body of the parent grows out as a bud which then detaches and becomes a new organism.
(i) Fission, e.g. Amoeba (ii) Fragmentation, e.g. Spirogyra
(iii) Regeneration, e.g. Planaria (iv) Budding, e.g. Hydra
Binary fission: It is the division of one cell into two similar cells. In this method, the nucleus first divides amitotically into two, followed by the division of the cytoplasm. The cell finally splits into two daughter cells.
Budding: In budding, a small part of the body of the parent grows out as a bud which then detaches and becomes a new organism.
116. (a) What is pollination? Explain its
significance.
(b) Explain the process of fertilisation in flowers. Name the parts of the flower that develops after fertilisation into (i) seed, (ii) fruit.
(b) Explain the process of fertilisation in flowers. Name the parts of the flower that develops after fertilisation into (i) seed, (ii) fruit.
Answer:
(a) It is the transfer of pollen grain from the anther of a flower to
the stigma of a carpel.
Significance of pollination:
(i) It is necessary for seed formation and thus, the perpetuation of species.
(ii) It stimulates the development of fruits.
Cross-pollination brings about genetic recombination of traits.
(b)
Significance of pollination:
(i) It is necessary for seed formation and thus, the perpetuation of species.
(ii) It stimulates the development of fruits.
Cross-pollination brings about genetic recombination of traits.
(b)
- After
the pollen lands on a suitable stigma, it has to reach the female germ
cells in the ovary.
- The pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain through the style to reach the
ovary.
- Male
germ cell travels through the pollen tube to reach the female germ cell
and fertilizes it.
- After
fertilisation, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule.
(i) Ovule becomes a seed.
(ii) Ovary becomes a fruit.
(ii) Ovary becomes a fruit.
117. (a) Name the human male reproductive organ
that produces sperms and also secretes hormones. Write the functions of the
hormone secreted.
(b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where (i) fertilization and
(ii) implantation occur respectively. Explain how the embryo gets nutrition inside the mother’s body. 5 👇
(b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where (i) fertilization and
(ii) implantation occur respectively. Explain how the embryo gets nutrition inside the mother’s body. 5 👇
Answer:
(a) The formation of sperms takes place in the testis. It secretes the
hormone, called testosterone. In addition to regulating the formation of
sperms, testosterone brings about changes in appearance seen in boys at the
time of puberty.
(b) (i) The fertilisation takes place in the fallopian tubes.
(ii) The implantation occurs in the uterus.
The uterus prepares itself every month to receive and nurture the growing embryo. The lining thickens and is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo.
The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called the placenta. The development of the child inside the mother’s body takes approximately nine months. On completion of nine months, the child is born due to rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus.
(b) (i) The fertilisation takes place in the fallopian tubes.
(ii) The implantation occurs in the uterus.
The uterus prepares itself every month to receive and nurture the growing embryo. The lining thickens and is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo.
The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called the placenta. The development of the child inside the mother’s body takes approximately nine months. On completion of nine months, the child is born due to rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus.
118. (a) What is pollination? How does it occur in
plants?
(b) How does pollination lead to fertilisation? Explain.
(c) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on the stigma of a flower.
(b) How does pollination lead to fertilisation? Explain.
(c) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on the stigma of a flower.
Answer: (a) It is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a
stamen to the stigma of a carpel. The pollen grains are transferred by many
agents, such as insects, birds, animals, wind and water.
Pollination is of two types – self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Self-Pollination. It is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same plant. It is seen in pea plant.
(b) Pollination is followed by fertilisation in plants. After the pollen lands on a suitable stigma, a pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain through the style to reach the ovary. Double fertilisation occurs inside each embryo sac, in which two fusions, syngamy and triple fusion take place. When one male gamete fuses with the egg contained in the embryo sac of the ovule, this fusion of male and female gametes is called syngamy and its product is the zygote. The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei and this process is called triple fusion, where three nuclei are involved.
After fertilisation, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule then develops a tough coat and gets converted into a seed. The seed contains the future embryo which develops into a seedling. The ovary develops and ripens to form a fruit.
Pollination is of two types – self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Self-Pollination. It is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same plant. It is seen in pea plant.
(b) Pollination is followed by fertilisation in plants. After the pollen lands on a suitable stigma, a pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain through the style to reach the ovary. Double fertilisation occurs inside each embryo sac, in which two fusions, syngamy and triple fusion take place. When one male gamete fuses with the egg contained in the embryo sac of the ovule, this fusion of male and female gametes is called syngamy and its product is the zygote. The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei and this process is called triple fusion, where three nuclei are involved.
After fertilisation, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule then develops a tough coat and gets converted into a seed. The seed contains the future embryo which develops into a seedling. The ovary develops and ripens to form a fruit.
119. (a) Give one example each of a unisexual and
a bisexual flower.
(b) How is the number of chromosomes of the parent cells maintained in the cells of the offsprings of sexually reproducing organisms?
(c) Mention the changes the flower undergoes after fertilization.
(b) How is the number of chromosomes of the parent cells maintained in the cells of the offsprings of sexually reproducing organisms?
(c) Mention the changes the flower undergoes after fertilization.
Answer:
(a) Papaya is a unisexual and Hibiscus is a bisexual flower.
(b) The parents are diploid (2n) as each of them has two sets of chromosomes. They form haploid (1n) male and female gametes through the process of meiosis. The haploid gametes have one set of chromosomes. These two gametes fuse during fertilization and the offspring become diploid (2n) which is same as parents chromosome number.
(c) After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat and gradually gets converted into the seed. The ovary grows rapidly to form a fruit. Meanwhile, the petals, sepals, stigma and style fall off.
(b) The parents are diploid (2n) as each of them has two sets of chromosomes. They form haploid (1n) male and female gametes through the process of meiosis. The haploid gametes have one set of chromosomes. These two gametes fuse during fertilization and the offspring become diploid (2n) which is same as parents chromosome number.
(c) After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat and gradually gets converted into the seed. The ovary grows rapidly to form a fruit. Meanwhile, the petals, sepals, stigma and style fall off.
120. Draw a longitudinal section of a flower and
label the following parts: 5 👇
(i) The part that produces pollen grain.
(ii) The part that transfers male gametes to the female gametes.
(iii) The part that is sticky to trap the pollen grain.
(iv) The part that develops into a fruit.
(i) The part that produces pollen grain.
(ii) The part that transfers male gametes to the female gametes.
(iii) The part that is sticky to trap the pollen grain.
(iv) The part that develops into a fruit.
Answer:
 |
| LONGITUDINAL SECTION OF A FLOWER |
121. (a) Write the functions of the following
parts in the human female reproductive system:
(i) Ovary (ii) Oviduct (iii) Uterus
(b) Describe the structure and function of the placenta. 5 👇
(i) Ovary (ii) Oviduct (iii) Uterus
(b) Describe the structure and function of the placenta. 5 👇
Answer:
(a) (i) Ovary:
(a) It produces female gamete.
(b) It secretes female sex hormones estrogen & progesterone.
(ii) Oviduct:
(a) It carries the egg from ovary to uterus.
(b) It allows sperm to travel to meet the egg.
(iii) Uterus:
(a) It allows implantation of zygote on its wall.
(b) It causes menstruation when the egg is not fertilized.
(b) After fertilisation, a special tissue develops between the uterine wall and the embryo (foetus) called the placenta, where the exchange of nutrients, glucose and oxygen takes place. The developing embryo will also generate waste substances which are removed by transferring them into the mother’s blood through the placenta. The development of the child inside the mother’s womb takes approximately nine months.
(a) It produces female gamete.
(b) It secretes female sex hormones estrogen & progesterone.
(ii) Oviduct:
(a) It carries the egg from ovary to uterus.
(b) It allows sperm to travel to meet the egg.
(iii) Uterus:
(a) It allows implantation of zygote on its wall.
(b) It causes menstruation when the egg is not fertilized.
(b) After fertilisation, a special tissue develops between the uterine wall and the embryo (foetus) called the placenta, where the exchange of nutrients, glucose and oxygen takes place. The developing embryo will also generate waste substances which are removed by transferring them into the mother’s blood through the placenta. The development of the child inside the mother’s womb takes approximately nine months.
122. (a) Why does fertilisation occur only once in
a month in a human female? Explain.
(b) Prenatal sex determination has been prohibited by law. State the necessity of enforcement of this law.
(c) Where are human testis located and why? State their functions. 5 👇
(b) Prenatal sex determination has been prohibited by law. State the necessity of enforcement of this law.
(c) Where are human testis located and why? State their functions. 5 👇
Answer:
(a) On attaining puberty, the eggs in the ovaries of a human female
start maturing. Only one egg is produced by one of the ovaries every month.
Fertilisation can, therefore, occur only once in a month in a human female.
(b) The most ideal female, the male sex ratio for a healthy society is 1000:1000.
Because of reckless female foeticide, sex ratio is decreasing at an alarming
rate in some sections of our society. It has, therefore, become necessary to ban
detection of the sex of the foetus.
(c) The testis is located outside the abdominal cavity inside the scrotum in a human male. The scrotum provides an optimum temperature for the formation of sperms.
(c) The testis is located outside the abdominal cavity inside the scrotum in a human male. The scrotum provides an optimum temperature for the formation of sperms.
123. Describe in brief the role of (i) testis (ii)
seminal vesicle, (iii) vas deferens, (iv) ureter and (v) prostate gland in the human male reproductive system.
Answer:
(i) Testis: Testes are oval-shaped primary reproductive organs in men.
The function of testes is to produce sperms and the male sex hormone testosterone.
The scrotum provides an optimal temperature for the formation of sperms.
(ii) Seminal vesicle: Seminal vesicles are a pair of thin-walled muscular elongated sac which secretes fluid for the nourishment of sperms.
(iii) Vas deferens: The sperms are carried by a long tube called vas deferens to organs called seminal vesicles where the sperms get nourishment and stored.
(iv) Ureter: It is the tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. In humans, there are two ureters, one attached to each kidney.
(v) Prostate gland: Prostate gland produces a fluid which is released in the urethra along with the secretion of seminal vesicles for nourishment and transportation of sperms.
(ii) Seminal vesicle: Seminal vesicles are a pair of thin-walled muscular elongated sac which secretes fluid for the nourishment of sperms.
(iii) Vas deferens: The sperms are carried by a long tube called vas deferens to organs called seminal vesicles where the sperms get nourishment and stored.
(iv) Ureter: It is the tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. In humans, there are two ureters, one attached to each kidney.
(v) Prostate gland: Prostate gland produces a fluid which is released in the urethra along with the secretion of seminal vesicles for nourishment and transportation of sperms.
124. Draw a diagram of a human female reproductive
system and label the part
(i) that produces egg (ii) where the fusion of egg and sperm takes place
(iii) where the zygote is implanted
What happens to a human egg when it is not fertilised?
(i) that produces egg (ii) where the fusion of egg and sperm takes place
(iii) where the zygote is implanted
What happens to a human egg when it is not fertilised?
Answer:
If the egg is not fertilized, the thick and nourishing lining of the
uterus breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous.
125. State in brief the changes that take place in
a fertilised egg (zygote) till the birth of the child in the human female
reproductive system. What happens to the egg when it is not fertilised?
Answer: The egg gets fertilised in the oviduct. The fertilised egg, the
zygote, gets implanted in the lining of the uterus and starts dividing. The
uterus prepares itself every month to receive and nurture the growing embryo.
Its lining thickens and is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing
embryo.
The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called the placenta. The development of the child inside the mother’s body takes approximately nine months. On completion of 9 months, the child is born as a result of rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus.
If the egg is not fertilized, the thick and nourishing lining of the uterus breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous.
The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called the placenta. The development of the child inside the mother’s body takes approximately nine months. On completion of 9 months, the child is born as a result of rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus.
If the egg is not fertilized, the thick and nourishing lining of the uterus breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous.
How do Organisms Reproduce?
126. (a) What is the spore formation? 5 👇
(b) Draw a diagram showing spore formation in Rhizopus.
(c) List two advantages for organisms to reproduce themselves through spores.
(b) Draw a diagram showing spore formation in Rhizopus.
(c) List two advantages for organisms to reproduce themselves through spores.
Answer:
(a) Spore formation: When a slice of bread is kept in a moist dark place
for a few days, spores of Rhizopus present in the air settle on the bread to form new
fungus plants of Rhizopus.
The Rhizopus consists of fine thread-like projections called hyphae. It has a knob-like structures which are involved in reproduction called sporangia, containing spores, that develop into new Rhizopus.
The Rhizopus consists of fine thread-like projections called hyphae. It has a knob-like structures which are involved in reproduction called sporangia, containing spores, that develop into new Rhizopus.
 |
| SPORE FORMATION IN RHIZOPUS |
c) Two advantages for organisms to reproduce themselves through spores
are as follows:
(i) It is a faster mode of reproduction.
(ii) Offsprings produced are identical.
(i) It is a faster mode of reproduction.
(ii) Offsprings produced are identical.
127. Argha is a 14 years old girl born in a poor
family of 6 members. She is the eldest of the 4 children of her parents.
Finding it difficult to feed a family of six, Argha’s father has arranged
Argha’s marriage with a boy in a nearby village. Argha, however, does not want to
get married at such a young age. She goes to the village headman and requests
him to save her from the problem. The village headman knows the financial
condition of Argha’s parents and at the same time, he knows that 14 years is a too
young age to get married.
(a) What should the headman do to solve Argha’s problem?
(b) What do the young couples learn from Argha’s story ? 4
(a) What should the headman do to solve Argha’s problem?
(b) What do the young couples learn from Argha’s story ? 4
Answer:
(a) There are various
schemes of the Government viz. Jawahar Rojgar Yojna, etc. which ensure a
minimum wage-earning to a person. As village headman, he should organise the implementation of such beneficial schemes in the village which will reduce the
financial problem of Argha’s parents. He then has to explain Argha’s parents
that Argha is not yet physically and mentally ready to get married. She should
be given more time to her mind and body mature.
(b) They should not have more than 1 or 2 children so that they can look after their children and the children do not become a burden to the increasing population of the
(b) They should not have more than 1 or 2 children so that they can look after their children and the children do not become a burden to the increasing population of the
128. A newspaper has recently published a survey
result which says that a number of AIDS patients in the country is increasing every day. The report also says that awareness among people about AIDS is still
very poor. You discussed the newspaper report with your friend and both of you
decided to help people to fight against this deadly disease.
(a) What problem do you anticipate if both of you try to educate the people of your village?
(b) How will you overcome that problem?
(a) What problem do you anticipate if both of you try to educate the people of your village?
(b) How will you overcome that problem?
Answer:
(a) The people of the village may not accept us as educators to teach
them about their sexual behaviour.
(b) We will make a slightly bigger group by including more people. We will then meet the civil SDO, medical officers and other senior government officers and request them to address the villagers in a public meeting on the topic of AIDS. The sub-divisional officer will be requested to supply awareness posters on AIDS and we will volunteer ourselves to stick the posters in the village. Once people find us working together with the government on a cause, they will slowly accept us and then onwards we will talk to the people directly on AIDS.
(b) We will make a slightly bigger group by including more people. We will then meet the civil SDO, medical officers and other senior government officers and request them to address the villagers in a public meeting on the topic of AIDS. The sub-divisional officer will be requested to supply awareness posters on AIDS and we will volunteer ourselves to stick the posters in the village. Once people find us working together with the government on a cause, they will slowly accept us and then onwards we will talk to the people directly on AIDS.
129. Reena was not keeping well. Her doctor after
examination told her that she was suffering from dysentery. The doctor gave her
medicines and advised her to take lots of fluids.
(a) What advice will you give to the people to protect them against dysentery?
(b) Why did the doctor advise Reena to drink lots of liquid?
(c) What action should the government take to stop spreading of diseases like dysentery?
(a) What advice will you give to the people to protect them against dysentery?
(b) Why did the doctor advise Reena to drink lots of liquid?
(c) What action should the government take to stop spreading of diseases like dysentery?
Answer:
(a) The people will be advised to drink clean water only, and if
possible drink water after boiling.
(b) Dysentery causes dehydration and hence, drinking lots of liquid is essential.
(c) (i) The government should arrange a supply of clean treated drinking water.
(ii) The government should ensure sanitary latrine in every household.
(b) Dysentery causes dehydration and hence, drinking lots of liquid is essential.
(c) (i) The government should arrange a supply of clean treated drinking water.
(ii) The government should ensure sanitary latrine in every household.
130. Riyan brought a male and a female dog
from a cold city of Switzerland to his home in Delhi. During summer, the dogs
appeared very tired and Riyan had to switch on the fan occasionally. The dogs
were allowed to reproduce and Riyan noticed that few 3rd generation dogs were
very comfortable in Delhi summer.
(a) How can you explain the adaptability of the dogs to Delhi summer?
(b) How did Riyan help the dogs to adapt to the changing environment? What value does the act convey?
(c) What will happen if the 3rd generation heat resistant dogs are shifted to the cold city of Switzerland? 4
(a) How can you explain the adaptability of the dogs to Delhi summer?
(b) How did Riyan help the dogs to adapt to the changing environment? What value does the act convey?
(c) What will happen if the 3rd generation heat resistant dogs are shifted to the cold city of Switzerland? 4
Answer:
(a) DNA copying is not perfect during sexual reproduction and produces
variation in the offspring. Over the generations, the variations get
accumulated and give rise to a species who can tolerate heat.
(b) Riyan helped the dogs to adjust to the changing environment by switching on the fan occasionally. The act conveys love towards animals.
(c) The dogs will reproduce sexually to give rise to offspring. The offspring will again reproduce to give rise to new offspring. DNA copying during sexual reproduction will not be perfect and the little variation will get accumulated over generations.
Accumulated variation may give rise to a species who is cold resistant.
(b) Riyan helped the dogs to adjust to the changing environment by switching on the fan occasionally. The act conveys love towards animals.
(c) The dogs will reproduce sexually to give rise to offspring. The offspring will again reproduce to give rise to new offspring. DNA copying during sexual reproduction will not be perfect and the little variation will get accumulated over generations.
Accumulated variation may give rise to a species who is cold resistant.
How do Organisms Reproduce?
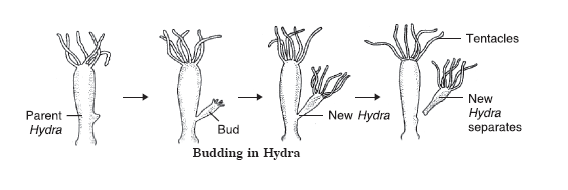
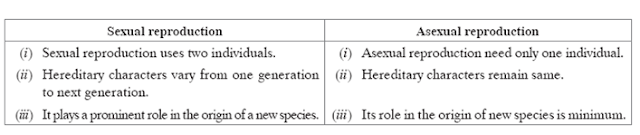




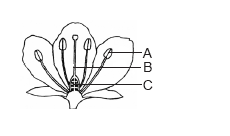





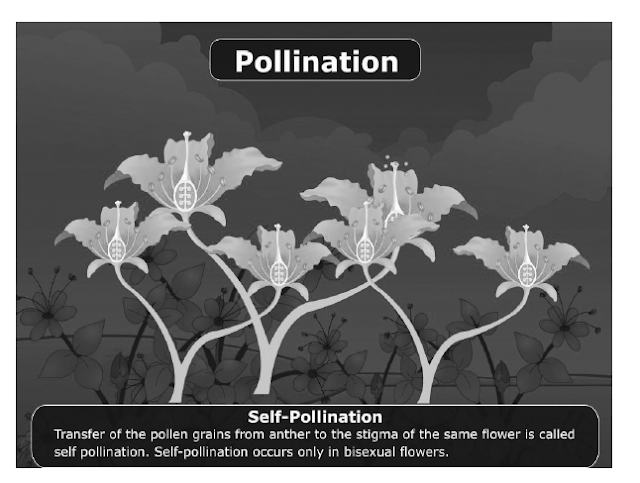












0 comments:
Post a Comment