 |
| CELLS |
NCERT SCIENCE
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF
LIFE
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
1.
Name the cell organelle which is termed
as the powerhouse of the cell. 1
Answer: Mitochondria.
2.
Which part of the plant cell permits it
to withstand very dilute external medium without bursting? 1
Answer:
Cell wall permits cells to withstand very
dilute external medium without bursting.
3.
Identify the single-celled organisms
from the following: 1
Cockroach, Chlamydomonas, snake, mosquito, bacteria
Cockroach, Chlamydomonas, snake, mosquito, bacteria
Answer:
Chlamydomonas and bacteria are single-celled organisms.
4.
Write any two differences between
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 1
Answer:
Differences:
Prokaryotic Cell
|
Eukaryotic Cell
|
(i) Size: generally small (1-10
µm). [1µm = 10–6 m]
|
(i) Size: generally large
(5-100 µm).
|
(ii) Nuclear region: poorly defined due to the absence of the nuclear envelope and known as the nucleoid.
|
(ii) Nuclear region: well defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
|
5.
What are the basic functions of a cell? 1
Answer: The basic functions of a cell are
respiration, nutrition, reproduction, etc. which are essential for survival.
6.
When a living plant cell loses water
through osmosis, there is a contraction of the contents of the cell away from the
cell wall. What is this phenomenon called?
1
Answer: The phenomenon is known as
plasmolysis.
7.
List the constituents of the plasma
membrane. 1
Answer: Plasma membrane is made up of proteins
and lipids.
8.
Name the process in which diffusion
takes place through a selectively permeable membrane. 1
Answer: Osmosis.
9.
Define diffusion. 1
Answer: Diffusion is the spontaneous movement
of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region of low
concentration.
10.
Name two factors on which shape of the
cell depends. 1
Answer: Shape of the cell depends upon
functional adaptations and viscosity of the protoplasm.
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
11.
What is the chemical composition of the cell wall in plants and fungi? 1
Answer: Cell wall in plants is made up of
cellulose whereas in fungi it is made up of chitin.
12.
State the function of the chromosome in a
cell. 1
Answer: Chromosomes contain information for
inheritance of features from parents to next generation in the form of DNA
molecules.
13.
Name the functional unit of DNA that
carries genetic information. 1
Answer: Genes are functional units of DNA.
14.
Give the term for the incipient nucleus
of prokaryotes. 1
Answer: Nucleoid.
15. Why is the nucleus called “director of the
cell”? 1
Answer: The nucleus controls and coordinates
all the metabolic functions of the cell.
16.
Name two cell organelles that have
their own genetic material. 1
Answer: Two cell organelles that have their
own genetic materials are mitochondria and plastids.
17.
Name the cell organelle which is able
to destroy a damaged cell. 1
Answer: Lysosomes.
18.
Give a one-word answer to the following: 1
(i) Organelle containing chlorophyll.
(ii) Living matter of the cell.
(iii) A cell without a membrane-bound nucleus.
(iv) An organelle with cristae.
(i) Organelle containing chlorophyll.
(ii) Living matter of the cell.
(iii) A cell without a membrane-bound nucleus.
(iv) An organelle with cristae.
Answer:
(i) Chloroplast
(ii) Protoplasm
(iii) Prokaryotic cell
(iii) Prokaryotic cell
(iv) Mitochondria
19. Name the process by which
unicellular freshwater organisms and most plant cells fend to gain water. 1
Answer: Osmosis.
20.
In which parts of the plant are
chromoplasts found? 1
Answer: Chromoplasts are found in petals of
flowers and fruits.
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
21.
Which cell organelle is responsible for
the release of energy as ATP? 1
Answer: Mitochondria.
22.
Which type of ribosomes are found in
prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 1
Answer: Prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes and eukaryotes
have 80S ribosomes.
23.
Why are ribosomes called ‘protein
factories’? 1
Answer: These are sites of protein synthesis.
24.
Name the substance which gives green
colour to the leaves of plants. 1
Answer: Chlorophyll.
25.
What is the name of the Golgi apparatus in
a plant cell ? 1
Answer: Dictyosome.
26. ‘Every multicellular organism has arisen from a single cell’. Justify
this statement. 1
Answer: Cells
divide to produce cells of their own kind. Thus, all cells come from
preexisting cells and hence every multicellular organism has arisen from a
single cell.
27.
The shape and size of cells are related
to the specific function they perform. Justify the given statement with a suitable
example. 1
Answer: Amoeba can change its
shape to perform its functions.
A nerve cell is elongated and has a typical shape to suit its function of transmission of signals.
Thus, the shape and size of cells are related to the specific function they perform.
A nerve cell is elongated and has a typical shape to suit its function of transmission of signals.
Thus, the shape and size of cells are related to the specific function they perform.
28.
What is plasmolysis? 1
Answer: When a living plant cell is kept in a
hypertonic solution, it loses water through osmosis, there is shrinkage or
contraction of the content of the cell away from the cell wall. This phenomenon
is known as plasmolysis.
29.
What would happen, if there is an
absence of a cell wall in a plant cell? 1
Answer: Plant cell wall is made up of
cellulose which provides strength. In the absence of a cell wall, the plant will
not have this structural strength.
30.
Give a reason why plastids are able to
make their own protein. 1
Answer: Plastids have their own DNA and hence can
make their own protein.
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
31.
Which is the smallest cell in the human
body? 1
Answer: Human sperm is the smallest cell in
human body.
32.
Name the largest cell in the human body? 1
Answer: Female ovum or egg is the largest cell
in the human body.
33.
Give two examples of organisms in which
a single cell performs all the functions.
OR
Name two unicellular organisms. 1
Answer: Amoeba and Paramoecium.
34.
Draw a neat and well-labelled diagram
of a typical prokaryotic cell. 3
Answer:
35.
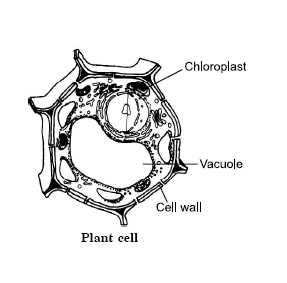
Draw the diagram of a plant cell and
label any three parts which make it different from an animal cell. 3
Answer:
Label: cell wall, large vacuole, chloroplast.
36. Distinguish between hypotonic solution, isotonic solution and hypertonic
solution. 3
Answer: Hypotonic
Solution: If the medium surrounding the cell has a higher water concentration
than the cell, i.e. if the solution is very dilute, the cell will gain water by
osmosis. Such a dilute solution is called a hypotonic solution.
Isotonic Solution: If the medium has exactly the same water concentration as the cell, there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane. Such a solution is known as an isotonic solution.
Hypertonic Solution: If the medium surrounding the cell has a lower concentration of water than the cell, i.e. if it is a very concentrated solution, the cell will lose water by osmosis. Such a solution is called a hypertonic solution.
Isotonic Solution: If the medium has exactly the same water concentration as the cell, there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane. Such a solution is known as an isotonic solution.
Hypertonic Solution: If the medium surrounding the cell has a lower concentration of water than the cell, i.e. if it is a very concentrated solution, the cell will lose water by osmosis. Such a solution is called a hypertonic solution.
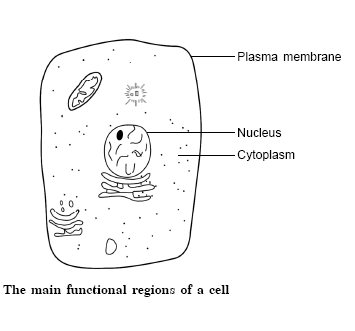
37. What are the main functional regions of a cell? Explain with the help of
a diagram. 3
Answer:
There are three main functional regions of a
cell, as shown in the diagram.
(a) Plasma membrane (PM): It is flexible and
made up of phospholipid bilayer that consists of proteins and lipids which
surrounds the cell and is semipermeable in nature.
(b) Cytoplasm: It is an amorphous and homogeneous colloidal ground substance present between the PM and nucleus.
(c) Nucleus: It is centrally located, spherical prominent organelle surrounded by two unit membranes, which is responsible for controlling all vital activities of a cell. It also contains genetic material.
(b) Cytoplasm: It is an amorphous and homogeneous colloidal ground substance present between the PM and nucleus.
(c) Nucleus: It is centrally located, spherical prominent organelle surrounded by two unit membranes, which is responsible for controlling all vital activities of a cell. It also contains genetic material.
38.
Describe the complexity in the structure of
organisms. 3
Answer: In organisms, there is much complexity
in structure. Some organisms are single-celled and they are called unicellular organisms such as Amoeba and Paramoecium.
In such organisms, single-cell performs all the functions.
Some organisms have many cells in their structure. They are called multicellular organisms, such as human, animals, trees, etc. In multicellular organisms, special structures perform special functions. Example: In plants, green leaves synthesise food, roots absorb water.
Some organisms have many cells in their structure. They are called multicellular organisms, such as human, animals, trees, etc. In multicellular organisms, special structures perform special functions. Example: In plants, green leaves synthesise food, roots absorb water.
39.
What is the difference between the plasma
membrane and cell wall? Give the functions of each one.
OR
State three differences between the cell membrane and
cell wall. 3
Answer:
Cell wall
|
Plasma or Cell membrane
|
(i) It is present in plant cells only.
|
(i) It is present in both animal and plant cells.
|
(ii) It is the outermost covering of plant cells.
|
(ii) It is the outermost covering of animal cells.
|
(iii) It is present outside the plasma membrane.
|
(iii) It is present outside the cytoplasm.
|
(iv) The cell wall is rigid and comparatively thick.
|
(iv) The plasma membrane is flexible and comparatively
thin. |
(v) It is non-living and permeable.
|
(v) It is living and selectively permeable.
|
(vi) It is made up of cellulose.
|
(vi) It is made up of lipids and proteins.
|
The function of plasma membrane: It acts as a semipermeable membrane which allows only selective substances to pass through
it.
The function of the cell wall: It provides rigidity and protection to the cell.
The function of the cell wall: It provides rigidity and protection to the cell.
40.
(a) Write two points of difference
between the nuclear region of a bacterial cell and nuclear region of an animal
cell.
(b) Which structure present in the nuclear region of a living cell bear genes? 3
(b) Which structure present in the nuclear region of a living cell bear genes? 3
Answer:
(a) Differences:
Nuclear region of a bacterial cell
(Prokaryotic cell) |
Nuclear region of an animal cell
(Eukaryotic cell) |
(i) Nuclear the region is poorly defined due to the absence of membrane and known as the nucleoid.
|
(i) The nuclear region is well-defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
|
(ii) The nucleolus is absent.
|
(ii) The nucleolus is present.
|
(b) Chromosomes bear genes.
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
41. Which organelle is the most prominent and important structure in a cell,
and also acts as the control centre of the cell and why? 3
Answer: The
most important and prominent structure in a cell, which also acts as the
control centre is the nucleus. It is called so because it contains genetic material
which is responsible for carrying hereditary information from one generation to
another. Besides this, it also regulates and controls various metabolic and
vital activities of the cell.
42.
Define the following terms:
Protoplasm, cytoplasm, nucleoplasm 3
Protoplasm, cytoplasm, nucleoplasm 3
Answer: Protoplasm: It refers to the living
substance present in the living cells consisting of cytoplasm and nucleoplasm.
Cytoplasm: It is a part of protoplasm filled within the space between nuclear membrane and cell membrane having cell organelles. It is viscous and homogenous containing water, glucose, oxygen, amino acids, etc.
Nucleoplasm: The space between the nuclear membrane and nucleolus is filled with a transparent semi-fluid substance called nucleoplasm. It consists of nucleic acids, basic and acidic proteins, lipids and minerals.
Cytoplasm: It is a part of protoplasm filled within the space between nuclear membrane and cell membrane having cell organelles. It is viscous and homogenous containing water, glucose, oxygen, amino acids, etc.
Nucleoplasm: The space between the nuclear membrane and nucleolus is filled with a transparent semi-fluid substance called nucleoplasm. It consists of nucleic acids, basic and acidic proteins, lipids and minerals.
43.
Name the cell organelles which are
called ‘suicide bags’ and ‘power-house’ of the cell. Why are they called so?
Give reason. 3
Answer: Lysosomes are called ‘suicide bags’ of
the cell as they can digest the entire damaged or dead cell containing them.
Mitochondria are called ‘powerhouse’ of the cell as they are sites for synthesis of energy-rich ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) molecules by cellular respiration.
Mitochondria are called ‘powerhouse’ of the cell as they are sites for synthesis of energy-rich ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) molecules by cellular respiration.
44.
What are lysosomes, peroxisomes and
centrosomes? Write their functions. 3
Answer: Lysosomes: They are single-membraned
small vesicular structures found in the cytoplasm of all the eukaryotic cells
except mammalian RBC’s. They contain enzymes and are formed by the Golgi apparatus.
Functions: They are involved in the intracellular digestion of foreign food or microbes and are also involved in autolysis or self-digestion of cells after their death.
Peroxisomes: They are found in photosynthetic cells of plants, liver and kidney cells of the vertebrates and contain two types of oxidative enzymes: oxidase and catalase, bounded by a unit membrane.
Functions: These are involved in the removal of toxic substances by oxidative reactions. In the plant cells, these also help in photorespiration.
Centrosome: A centrosome is a light microscopic organelle formed of two darkly coloured granules called centrioles surrounded by a transparent cytoplasmic area called centrosphere. It lies near the nucleus and is commonly called cell centre.
Functions: Centrosome helps in cell division in animal cells. They also help in the formation of cilia and flagella of the cells.
Functions: They are involved in the intracellular digestion of foreign food or microbes and are also involved in autolysis or self-digestion of cells after their death.
Peroxisomes: They are found in photosynthetic cells of plants, liver and kidney cells of the vertebrates and contain two types of oxidative enzymes: oxidase and catalase, bounded by a unit membrane.
Functions: These are involved in the removal of toxic substances by oxidative reactions. In the plant cells, these also help in photorespiration.
Centrosome: A centrosome is a light microscopic organelle formed of two darkly coloured granules called centrioles surrounded by a transparent cytoplasmic area called centrosphere. It lies near the nucleus and is commonly called cell centre.
Functions: Centrosome helps in cell division in animal cells. They also help in the formation of cilia and flagella of the cells.
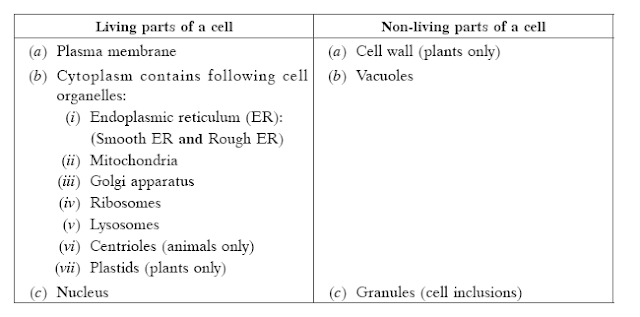
45.
Name the different living and
non-living parts of a cell or cell organelles.
3
Answer:
The different living and non-living cell
organelles are:
46.
What will happen if we put an animal
cell or a plant cell into a solution of sugar in the water? 3
Answer: If we put an animal cell into a
solution of sugar, one of the following three things may happen:
(i) If the medium surrounding the cell has higher water concentration than the cell, then the cell will gain water by osmosis.
(ii) If the medium has exactly the same water concentration as the cell, there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane.
(iii) If the medium has a lower concentration of water than the cell, then the cell will lose water by osmosis.
(i) If the medium surrounding the cell has higher water concentration than the cell, then the cell will gain water by osmosis.
(ii) If the medium has exactly the same water concentration as the cell, there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane.
(iii) If the medium has a lower concentration of water than the cell, then the cell will lose water by osmosis.
47. The grass looks green, papaya appears
yellow. Which cell organelle is responsible for this? 3
Answer: Plastids
These are found in plant cells only. Plastids
are the major cell organelles in plants. On the basis of pigments present in
plastids, they are divided into two types (i) the colourless leucoplasts and
(ii) the pigmented chromoplasts. The colourless leucoplasts store starch, oil
and protein granules whereas the pigmented chromoplasts have different colours
and can be of several types. The most important ones are those containing the
pigment chlorophyll, known as chloroplasts, which is responsible for the
preparation of food by photosynthesis. Other chromoplasts contain non-green
pigments, which are responsible for the characteristic colours of fruits and
flowers.
48.
Where are chromosomes located? What are
they composed of? What is chromatin material and how does it change just before
the cell divides? 3
Answer: Chromosomes are located in the nucleus
of plant and animal cells.
They are composed of DNA and protein. Chromatin material is entangled mass of thread-like structures. The chromatin material gets organised into chromosomes just before the cell divides.
They are composed of DNA and protein. Chromatin material is entangled mass of thread-like structures. The chromatin material gets organised into chromosomes just before the cell divides.
49.
What does the DNA molecule contain? Name
the functional segment of DNA. In which form is the DNA present in a cell when
the cell is not dividing? 3
Answer: DNA molecules contain the information
necessary for construction and organisation of cells.
Functional segments of DNA are called genes. In a cell which is not dividing, DNA is present as a part of chromatin material.
Functional segments of DNA are called genes. In a cell which is not dividing, DNA is present as a part of chromatin material.
50.
Differentiate between diffusion and
osmosis. 4
Answer:
Diffusion
|
Osmosis
|
(i) Diffusion takes place in any medium.
|
(i) Osmosis occurs only in a liquid medium.
|
(ii) It is the movement of a substance from the area of its higher concentration to the area of its lower concentration.
|
(ii) It is the movement of water from the area of its higher water concentration to the area of lower concentration.
|
(iii) The diffusing molecules may be solids, liquids or gases.
|
(iii) It involves the movement of solvent molecules only.
|
(iv) It does not require a semi-permeable membrane.
|
(iv) It requires a semi-permeable membrane.
|
| NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9 | |
51. Name: 3
(a) An organelle which has its own genetic material
(b) An organelle rich in digestive enzymes
(c) Nucleic acid present in the nucleus of the cell
(a) An organelle which has its own genetic material
(b) An organelle rich in digestive enzymes
(c) Nucleic acid present in the nucleus of the cell
Answer:
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Lysosomes
(c) DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid).
(b) Lysosomes
(c) DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid).
52. How does a living cell perform the basic functions? 3
Answer: Each
cell has specific cell organelle to perform various functions. Some cell
organelle makes new materials in the cell, some clears waste material from a cell
and so on. These organelles together constitute the basic unit called a cell. A
cell is able to live and perform all its functions because of these organelles.
53.
Given below is a diagrammatic sketch of
electron microscopic view of an animal cell :
(a) Label the parts indicated by lines as 1 to 10. 5
(b) Give two reasons to support that it is an animal cell.
(c) How many mitochondria are shown in the diagram?
(a) Label the parts indicated by lines as 1 to 10. 5
(b) Give two reasons to support that it is an animal cell.
(c) How many mitochondria are shown in the diagram?
Answer:
(a) 1 – Cell membrane
2 – Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
3 – Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
4 – Lysosome
5 – Nucleolus
6 – Nucleus
7 – Nuclear envelope
8 – Golgi body
9 – Mitochondrion
10 – Cytoplasm
2 – Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
3 – Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
4 – Lysosome
5 – Nucleolus
6 – Nucleus
7 – Nuclear envelope
8 – Golgi body
9 – Mitochondrion
10 – Cytoplasm
(b) It is an animal cell because:
(i) A cell wall of cellulose is absent.
(ii) It has no definite shape but with prominent and well-developed Golgi bodies.
(c) Two mitochondria are shown in the diagram.
(i) A cell wall of cellulose is absent.
(ii) It has no definite shape but with prominent and well-developed Golgi bodies.
(c) Two mitochondria are shown in the diagram.
54.
Given below is a diagrammatic sketch of
a certain generalised cell. 5
(a) Name the parts numbered as 1 to 8.
(b) Is it a plant cell or an animal cell? Give two reasons in support of your answer.
(c) Give the functions of parts marked as 1, 6 and 8.
(a) Name the parts numbered as 1 to 8.
(b) Is it a plant cell or an animal cell? Give two reasons in support of your answer.
(c) Give the functions of parts marked as 1, 6 and 8.
Answer:
(a) 1 – Chloroplast
2 – Vacuole
3 – Mitochondrion
4 – Cytoplasm
5 – Nucleolus
6 – Nucleus
7 – Cell membrane
8 – Cell wall
2 – Vacuole
3 – Mitochondrion
4 – Cytoplasm
5 – Nucleolus
6 – Nucleus
7 – Cell membrane
8 – Cell wall
(b) It is a plant cell because:
(i) It has a definite shape with the cell wall.
(ii) The chloroplast is present.
(i) It has a definite shape with the cell wall.
(ii) The chloroplast is present.
(c) Functions:
1 – Chloroplast: They synthesise food by trapping solar energy so they are called “kitchen of the cell”.
6 – Nucleus: It controls all the activities of the cell so it is called “control centre of the cell”.
8 – Cell wall: It protects the plasma membrane and internal structures of the cell and helps in transporting various substances in and out of the cell.
1 – Chloroplast: They synthesise food by trapping solar energy so they are called “kitchen of the cell”.
6 – Nucleus: It controls all the activities of the cell so it is called “control centre of the cell”.
8 – Cell wall: It protects the plasma membrane and internal structures of the cell and helps in transporting various substances in and out of the cell.
55.
What are the main functions of each of
the following cell components? 5
(a) Plasma membrane
(b) Chromosomes
(c) Lysosomes
(d) Ribosomes
(e) Nucleus
(f) Mitochondria
(g) Nucleolus
(h) Cell wall
(i) Chloroplast
( j) Peroxisomes
(a) Plasma membrane
(b) Chromosomes
(c) Lysosomes
(d) Ribosomes
(e) Nucleus
(f) Mitochondria
(g) Nucleolus
(h) Cell wall
(i) Chloroplast
( j) Peroxisomes
Answer:
(a) Plasma membrane: It acts as a
semipermeable membrane and allows only selective substances to pass through it.
(b) Chromosomes: They carry hereditary characters from parents to offsprings, i.e. from one generation to another.
(c) Lysosomes: They act as ‘digestive bags’ which fight against any infection inside the cell.
(d) Ribosomes: They help in protein synthesis.
(e) Nucleus: It controls all metabolic activities of the cell.
(f) Mitochondria: It is the ‘power-house’ of the cell which stores and releases the energy in the form of ATP.
(g) Nucleolus: It acts as a platform for protein synthesis.
(h) Cell wall: It provides rigidity and protection to the cell.
(i) Chloroplast: It carries out photosynthesis in plants and synthesises food by trapping solar energy. So, they are called “kitchen of the cell”.
(j) Peroxisomes: It carries out oxidative reactions, which also remove the toxic substances.
(b) Chromosomes: They carry hereditary characters from parents to offsprings, i.e. from one generation to another.
(c) Lysosomes: They act as ‘digestive bags’ which fight against any infection inside the cell.
(d) Ribosomes: They help in protein synthesis.
(e) Nucleus: It controls all metabolic activities of the cell.
(f) Mitochondria: It is the ‘power-house’ of the cell which stores and releases the energy in the form of ATP.
(g) Nucleolus: It acts as a platform for protein synthesis.
(h) Cell wall: It provides rigidity and protection to the cell.
(i) Chloroplast: It carries out photosynthesis in plants and synthesises food by trapping solar energy. So, they are called “kitchen of the cell”.
(j) Peroxisomes: It carries out oxidative reactions, which also remove the toxic substances.
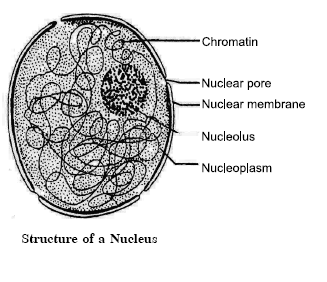
56.
Describe the structure of the nucleus.
OR
Explain in detail what do you know about the
structure of the nucleus. 5
Answer:
Robert Brown in 1831 discovered the nucleus in
the cell. The nucleus is the largest cell structure. It is spherical or oval in
shape and is a prominent structure. It is usually located in the centre of the
cell. Nucleus has the following important parts:
(i) Nuclear membrane: It is a double-layered
membrane, which separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
(ii) Nucleoplasm: It is a homogeneous and granular dense fluid present inside the nucleus, in which chromatin and nucleolus are suspended.
(iii) Chromatin material: It consists of a long, coiled network of thread-like structures. The chromatin material is made up of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which is responsible for storing and transmitting the hereditary information from one generation to the other. It condenses into compact rod-like bodies called chromosomes at the time of cell division.
(iv) Nucleolus: It is a more or less round structure found inside the nucleus. The nucleolus contains RNA (ribonucleic acid) and proteins. RNA is helpful in protein synthesis in the cytoplasm.
(ii) Nucleoplasm: It is a homogeneous and granular dense fluid present inside the nucleus, in which chromatin and nucleolus are suspended.
(iii) Chromatin material: It consists of a long, coiled network of thread-like structures. The chromatin material is made up of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which is responsible for storing and transmitting the hereditary information from one generation to the other. It condenses into compact rod-like bodies called chromosomes at the time of cell division.
(iv) Nucleolus: It is a more or less round structure found inside the nucleus. The nucleolus contains RNA (ribonucleic acid) and proteins. RNA is helpful in protein synthesis in the cytoplasm.
57.
How many membranes are present in
mitochondria? Give the characteristic features of these membranes. What is the
advantage of such features? 5
Answer: A mitochondrion contains outer and
inner membranes. The two membranes have different properties.
Characteristic feature:
Outer membrane: The outer mitochondrial membrane, which encloses the entire organelle, is 60 to 75 angstrom thick. It contains large numbers of porins which allow smaller molecules to diffuse from one side of the membrane to the other. Disruption of the outer membrane permits proteins in the intermembrane space to leak into the cytosol, leading to certain cell death. The mitochondrial outer membrane can associate with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane.
Inner membrane: It has a very high protein-to-phospholipid ratio. The inner membrane is home to around 1/5 of the total protein in a mitochondrion. In addition, the inner membrane is rich in cardiolipin. It makes inner membrane impermeable. All ions and molecules require special membrane transporters to enter or exit the matrix.
Advantages: Mitochondria are shaped perfectly to maximize their productivity. The folding of the inner membrane increases the surface area inside the organelle. Since many of the chemical reactions happen on the inner membrane, the increased surface area creates more space for reaction to occur.
Characteristic feature:
Outer membrane: The outer mitochondrial membrane, which encloses the entire organelle, is 60 to 75 angstrom thick. It contains large numbers of porins which allow smaller molecules to diffuse from one side of the membrane to the other. Disruption of the outer membrane permits proteins in the intermembrane space to leak into the cytosol, leading to certain cell death. The mitochondrial outer membrane can associate with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane.
Inner membrane: It has a very high protein-to-phospholipid ratio. The inner membrane is home to around 1/5 of the total protein in a mitochondrion. In addition, the inner membrane is rich in cardiolipin. It makes inner membrane impermeable. All ions and molecules require special membrane transporters to enter or exit the matrix.
Advantages: Mitochondria are shaped perfectly to maximize their productivity. The folding of the inner membrane increases the surface area inside the organelle. Since many of the chemical reactions happen on the inner membrane, the increased surface area creates more space for reaction to occur.
58.
Why is mitochondria called ‘power-house
of the cell’? Give three similarities and one difference between mitochondria and
plastid. 4
Answer: Mitochondria is called the
‘power-house of the cell’ because the energy required by various chemical activities
needed for life is released by mitochondria in the form of ATP. The body uses
energy stored in ATP for making new chemical compounds and for mechanical work.
Three similarities between mitochondria and plastid are:
(i) both mitochondria and plastids have their own DNA and ribosomes.
(ii) the external structure of mitochondria and plastids are the same.
(iii) both mitochondria and plastids have more than one membrane layer.
One difference between mitochondria and plastids is that mitochondria are present in both plant and animal cell whereas plastids are present only in the plant cell.
Three similarities between mitochondria and plastid are:
(i) both mitochondria and plastids have their own DNA and ribosomes.
(ii) the external structure of mitochondria and plastids are the same.
(iii) both mitochondria and plastids have more than one membrane layer.
One difference between mitochondria and plastids is that mitochondria are present in both plant and animal cell whereas plastids are present only in the plant cell.
59.
You are telling your 10 years old
sister that cells were discovered by Robert Hook in 1665, and based on his
observation, cell theory was developed. You do not have a microscope and hence
not able to show the structure of a cell to your sister. Your sister is too
small to understand this and asked you to show her a cell. 4
(i) What will you show to your sister which can give her an idea of a cell?
(ii) What is the life span of a cell?
(iii) What values are shown by you and your sister?
(i) What will you show to your sister which can give her an idea of a cell?
(ii) What is the life span of a cell?
(iii) What values are shown by you and your sister?
Answer:
(i) I can show her a beehive, each chamber of
which looks like a cell.
(ii) Different cells have a different life span. Some cells live for a few days whereas others live up to a year.
(iii) The value shown by me is to provide adequate information on the subject to my sister and to take a scientific approach to find a solution to a problem. The value shown by my sister is the curiosity to know things.
(ii) Different cells have a different life span. Some cells live for a few days whereas others live up to a year.
(iii) The value shown by me is to provide adequate information on the subject to my sister and to take a scientific approach to find a solution to a problem. The value shown by my sister is the curiosity to know things.
60.
You are told by your teacher that
plants have mostly dead cells in their body. On the other hand, most of the
animal cells are alive. A student wants to know from your teacher if it gives
an advantage to the organisms.
(i) What advantage do plants get by having mostly dead cells?
(ii) Why should we protect trees?
(iii) What value is shown by the student? 4
(i) What advantage do plants get by having mostly dead cells?
(ii) Why should we protect trees?
(iii) What value is shown by the student? 4
Answer:
(i) Plants are static. Dead cells give them
rigidity. They also do not need any energy to maintain dead cells.
(ii) We should protect the trees as trees give us oxygen to breathe.
They give us a cool breeze.
We get fruits, vegetables and many other food items from trees.
Trees help in conserving the biodiversity.
(iii) The value shown by the student is inquisitiveness and desire for knowledge.
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
(ii) We should protect the trees as trees give us oxygen to breathe.
They give us a cool breeze.
We get fruits, vegetables and many other food items from trees.
Trees help in conserving the biodiversity.
(iii) The value shown by the student is inquisitiveness and desire for knowledge.
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
61.
The structure/organelle of a cell that
functions as a passage for intracellular transport as well as a manufacturing
surface is 1
(i) ribosome
(ii) endoplasmic reticulum
(iii) plastids
(iv) plasma membrane
Answer: (ii)
62. If a plant cell is kept in a hypotonic solution, it will 1
(i) increase in its volume
(ii) maintain the same volume
(iii) decrease in its volume
(iv) burst
Answer: (i)
63.
Analyse the statements and pick up the
right one regarding mitochondrial membranes from the following: 1
(i) The inner membrane is longer
than the outer membrane
(ii) The outer membrane is longer than the inner membrane
(iii) Both the inner and outer membranes are almost equal in length.
(iv) Mostly mitochondria have a single membrane.
Answer: (i)
64.
The cell organelles (other than the
nucleus) which contain DNA are 1
(i) plastids and lysosomes
(ii) mitochondria and Golgi apparatus
(iii) Golgi apparatus and lysosomes
(iv) plastids and mitochondria
Answer: (iv)
65.
The primary function of smooth
endoplasmic reticulum in liver cells is
1
(i) protein synthesis
(ii) catabolism of proteins
(iii) detoxification
(iv) carbohydrate metabolism
Answer: (iii)
66.
Engulfing of food materials or foreign
bodies by cells like Amoeba is called 1
(i) diffusion
(ii) endocytosis
(iii) osmosis
(iv) plasmolysis
Answer: (ii)
67. In the plant cells, many substances
important for life are stored in 1
(i) plastids
(ii) mitochondria
(iii) vacuoles
(iv) lysosomes
Answer: (iii)
68. A prokaryotic cell does not possess 1
(i) cell membrane
(ii) cell wall
(iii) nuclear membrane
(iv) both (i) and (ii)
Answer: (iii)
69. The most abundant material in the plant
cell wall is 1
(i) cellulose
(ii) lipids
(iii) proteins
(iv) wax
Answer: (i)
70. The membrane of the Golgi apparatus has
connections with those of 1
(i) nuclear membrane
(ii) endoplasmic reticulum
(iii) cell membrane
(iv) mitochondria
Answer: (ii)
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
71. The major function of Golgi apparatus
is 1
(i) detoxification
(ii) fermentation
(iii) translocation
(iv) secretion
Answer: (iv)
72.The site of detoxification in liver cells is 1
(i) lysosome
(ii) RER
(iii) ribosome
(iv) SER
Answer: (iv)
73.
The cell organelles with digestive
enzymes are 1
(i) ribosomes
(ii) food vacuoles
(iii) lysosomes
(iv) Golgi apparatus
Answer: (iii)
74. The statement ‘cells arise only from
pre-existing cells’ was given by 1
(i) Schleiden
(ii) Rudolf Virchow
(iii) Schwann
(iv) Louis Pasteur
Answer: (ii)
75.
The term ‘protoplasm’ was coined by 1
(i) Schleiden
(ii) Purkinje
(iii) Schwann
(iv) Robert Brown
Answer: (ii)
76. 70-80 % of the volume of a mature plant
cell is occupied by 1
(i) endoplasmic reticulum
(ii) nucleus
(iii) cytoplasm
(iv) vacuole
Answer: (iv)
77. Rough endoplasmic reticulum helps in
the synthesis of 1
(i) glycogen
(ii) starch
(iii) steroids
(iv) proteins
Answer: (iv)
78. The fluid in the vacuole of a plant
cell is called 1
(i) cell sap
(ii) tonoplasm
(iii) cytoplasm
(iv) protoplasm
Answer: (i)
79. Lysosomes are formed by 1
(i) RER
(ii) plasma membrane
(iii) SER
(iv) Golgi apparatus
Answer: (iv)
80. Most of the substances in the living
world are transported across the cell membrane by the process of 1
(i) osmosis
(ii) endocytosis
(iii) diffusion
(iv) plasmolysis
Answer: (i)
81.
The proteins and lipids, essential for
building the cell membrane, are manufactured by 1
(i) rough endoplasmic
reticulum
(ii) Golgi apparatus
(iii) plasma membrane
(iv) mitochondria
Answer: (i)
82.
The undefined nuclear region of prokaryotes
are also known as 1
(i) nucleus
(ii) nucleolus
(iii) nucleic acid
(iv) nucleoid
Answer: (iv)
83. The cell organelle involved in forming
complex sugars from simple sugars are 1
(i) endoplasmic reticulum
(ii) ribosomes
(iii) plastids
(iv) Golgi apparatus
Answer: (iv)
84. Amoeba acquires its food through a
process termed 1
(i) exocytosis
(ii) endocytosis
(iii) plasmolysis
(iv) exocytosis and endocytosis both
Answer: (ii)
85. The cell wall of which one of these is not made
up of cellulose? 1
(i) Bacteria
(ii) Hydrilla
(iii) Mango tree
(iv) Cactus
Answer: (i)
86. Silver nitrate solution is used to
study 1
(i) endoplasmic reticulum
(ii) Golgi apparatus
(iii) nucleus
(iv) mitochondria
Answer: (ii)
87. Organelle other than nucleus,
containing DNA is 1
(i) endoplasmic reticulum
(ii) Golgi apparatus
(iii) mitochondria
(iv) lysosome
Answer: (iii)
88. The kitchen of the cells 1
(i) mitochondria
(ii) endoplasmic reticulum
(iii) chloroplast
(iv) Golgi apparatus
Answer: (iii)
89. Lipid molecules in the cell are
synthesized by 1
(i) smooth endoplasmic
reticulum
(ii) rough endoplasmic reticulum
(iii) Golgi apparatus
(iv) plastids
Answer: (i)
90. Lysosome arises from 1
(i) endoplasmic reticulum
(ii) Golgi apparatus
(iii) nucleus
(iv) mitochondria
Answer: (ii)
NCERT SCIENCE SOLUTION CLASS 9
91. Match the items of column A with those
of column B. 1
|
Column A
|
Column B
|
|
(i) Hypertonic solution
(ii) Selectively (iii) Cell (iv) Robert Brown (v) Suberin (vi) Prokaryotic cell |
1. Nucleoid
2. Little room permeable 3. Cork 4. Plasmolysis 5. Plasma membrane 6. Nucleus 7. Lysosome |
Answer: (i) – 4 (ii) – 5 (iii) – 2 (iv) –
6 (v) – 3 (vi) – 1
92.
There is no net movement of the water when
a cell is placed in a/an _________ medium.
1
Answer: isotonic.
93. The basic building units of an onion
bulb, are called ____________. 1
Answer: cells.
94. Membrane-bound cell organelles are not
found in ____________ cells. 1
Answer: prokaryotic.
95.
____________ are sites of protein
synthesis. 1
Answer: Ribosomes.
96. Centrosome helps in ____________
division. 1
Answer: cell.
97. Lysosomes are called as ‘suicide bags’
of a cell. [True/False] 1
Answer: True.
98. The folds of the inner membrane of
mitochondria increase the area for ATP generating chemical reactions.
[True/False] 1
Answer: True.
99.
Lysosomes are produced by the endoplasmic
reticulum. [True/False] 1
Answer: False.
100.
Chlamydomonas is a multicellular
organism. [True/False] 1
Answer: False.














0 comments:
Post a Comment